Abiotic Stresses: General Defenses of Land Plants and Chances for Engineering Multistress Tolerance
- PMID: 30581446
- PMCID: PMC6292871
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01771
Abiotic Stresses: General Defenses of Land Plants and Chances for Engineering Multistress Tolerance
Abstract
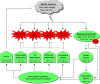
Abiotic stresses, such as low or high temperature, deficient or excessive water, high salinity, heavy metals, and ultraviolet radiation, are hostile to plant growth and development, leading to great crop yield penalty worldwide. It is getting imperative to equip crops with multistress tolerance to relieve the pressure of environmental changes and to meet the demand of population growth, as different abiotic stresses usually arise together in the field. The feasibility is raised as land plants actually have established more generalized defenses against abiotic stresses, including the cuticle outside plants, together with unsaturated fatty acids, reactive species scavengers, molecular chaperones, and compatible solutes inside cells. In stress response, they are orchestrated by a complex regulatory network involving upstream signaling molecules including stress hormones, reactive oxygen species, gasotransmitters, polyamines, phytochromes, and calcium, as well as downstream gene regulation factors, particularly transcription factors. In this review, we aimed at presenting an overview of these defensive systems and the regulatory network, with an eye to their practical potential via genetic engineering and/or exogenous application.
Keywords: abiotic stresses; general defenses; land plants; multistress tolerance; regulatory network.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad P., Abd Allah E. F., Alyemeni M. N., Wijaya L., Alam P., Bhardwaj R., et al. (2018). Exogenous application of calcium to 24-epibrassinosteroid pre-treated tomato seedlings mitigates NaCl toxicity by modifying ascorbate-glutathione cycle and secondary metabolites. Sci. Rep. 8:13515. 10.1038/s41598-018-31917-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- An J., Hou L., Li C., Wang C. X., Xia H., Zhao C. Z., et al. (2015). Cloning and expression analysis of four DELLA genes in peanut. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 62 116–126. 10.1134/s1021443715010021 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

