The relationship between 174 G/C and -572 G/C of IL-6 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility of celiac disease in the Iranian population
- PMID: 30581503
- PMCID: PMC6300853
- DOI: 10.5114/pg.2018.79808
The relationship between 174 G/C and -572 G/C of IL-6 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility of celiac disease in the Iranian population
Abstract
Introduction: Celiac disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder. Different immunological factors, including inflammatory cytokines, may play an important role in disease susceptibility.
Aim: To investigate the relationship between -174G/C and -572G/C gene polymorphisms and the serum level of interleukin 6 (IL-6) and susceptibility to CD in the Iranian population.
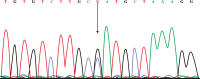
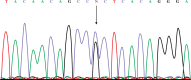
Material and methods: In this case-control study blood samples were collected of 105 patients with CD and 106 healthy subjects randomly in 2016 and evaluated by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragments length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) method. A sequence was also used to confirm the results of both polymorphisms. The IL-6 concentration was measured using ELISA.
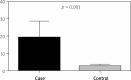
Results: The results showed a significant relationship between polymorphism -572G in CD patients when compared with control subjects by genotype (p = 0.001) and alleles (p = 0.022), respectively. There was no significant relationship between polymorphism 174G and frequency of genotype, but an association of this polymorphism with the frequency of alleles (p = 0.034), age (p = 0.001), and body mass index (p = 0.003) was seen. The serum level of interleukin-6 was significantly associated only with rs1800796 (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The results confirm previous studies in different parts of the world and indicate that IL-6 (572G/C) polymorphism may play a role in susceptibility to CD in the Iranian population.
Keywords: IL-6 gene polymorphism; autoimmune and inflammatory reaction; celiac disease; polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragments length polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 and interleukin-17 gene polymorphism association with celiac disease in children.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017 Nov;28(6):471-475. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2017.17092. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28928101
-
Effects of interleukin (IL)-6 gene polymorphisms on recurrent aphthous stomatitis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2014 Mar;306(2):173-80. doi: 10.1007/s00403-013-1406-x. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Arch Dermatol Res. 2014. PMID: 23982631
-
Promoter polymorphisms in IL-6 gene influence pro-inflammatory cytokines for the risk of osteoarthritis.Cytokine. 2020 Mar;127:154985. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.154985. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31951965
-
Association of IL-6 -174G>C and -572G>C Polymorphisms with Susceptibility to Cervical Cancer and Ovarian Cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Sep 1;22(9):2867-2871. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.9.2867. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 34582655 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between polymorphisms in -572G/C interleukin 6 promoter gene polymorphisms (rs1800796) and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Jan;23(1):47-54. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13729. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 31782615 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Genetic Polymorphisms and Serum Levels of IL-6 and IL-8 with the Prognosis in Children with Neuroblastoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 30;13(3):529. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030529. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33573284 Free PMC article.
-
Celiac Disease Increases the Risk of Multiple Sclerosis: Evidence from Mendelian Randomization and the Role of CCL19.Exp Neurobiol. 2025 Apr 30;34(2):63-76. doi: 10.5607/en25009. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Exp Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40229195 Free PMC article.
-
Toward finding the difference between untreated celiac disease and COVID-19 infected patients in terms of CD4, CD25 (IL-2 Rα), FOXP3 and IL-6 expressions as genes affecting immune homeostasis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Dec 11;21(1):462. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-02056-1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34895167 Free PMC article.
-
Association study of genetic variations of inflammatory biomarkers with susceptibility and severity of obstructive sleep apnea.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Aug;7(8):e801. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.801. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31210414 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of genetic association between celiac disease and type 1 diabetes.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024 May 5;23(1):1329-1336. doi: 10.1007/s40200-024-01429-z. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024. PMID: 38932832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dieterich W, Ehnis T, Bauer M, et al. Identification of tissue transglutaminase as the autoantigen of celiac disease. Nat Med. 1997;3:797–801. - PubMed
-
- Fasano A, Berti I, Gerarduzzi T, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the united states: a large multicenter study. Arch Inter Med. 2003;163:286–92. - PubMed
-
- Rincon M. Interleukin-6: from an inflammatory marker to a target for inflammatory diseases. Trends Immunol. 2012;33:571–7. - PubMed
-
- Clot F, Babron MC. Genetics of celiac disease. Mol Genet Metabol. 2000;71:76–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous