Smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy and toxicity studies: A review
- PMID: 30581608
- PMCID: PMC6300464
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2018.06.005
Smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy and toxicity studies: A review
Abstract
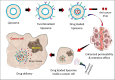
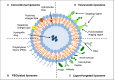
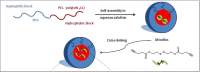
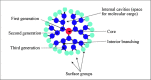
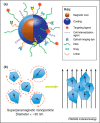
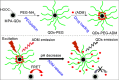
Nonspecific distribution and uncontrollable release of drugs in conventional drug delivery systems (CDDSs) have led to the development of smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems, which are also known as Smart Drug Delivery Systems (SDDSs). SDDSs can deliver drugs to the target sites with reduced dosage frequency and in a spatially controlled manner to mitigate the side effects experienced in CDDSs. Chemotherapy is widely used to treat cancer, which is the second leading cause of death worldwide. Site-specific drug delivery led to a keen interest in the SDDSs as an alternative to chemotherapy. Smart nanocarriers, nanoparticles used to carry drugs, are at the focus of SDDSs. A smart drug delivery system consists of smart nanocarriers, targeting mechanisms, and stimulus techniques. This review highlights the recent development of SDDSs for a number of smart nanocarriers, including liposomes, micelles, dendrimers, meso-porous silica nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles, super paramagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, and quantum dots. The nanocarriers are described in terms of their structures, classification, synthesis and degree of smartness. Even though SDDSs feature a number of advantages over chemotherapy, there are major concerns about the toxicity of smart nanocarriers; therefore, a substantial study on the toxicity and biocompatibility of the nanocarriers has been reported. Finally, the challenges and future research scope in the field of SDDSs are also presented. It is expected that this review will be widely useful for those who have been seeking new research directions in this field and for those who are about to start their studies in smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery.
Keywords: Cancer cell targeting; Drug release stimulus; Nanocarrier functionalization; Smart drug delivery; Smart nanocarrier; Toxicity of nanocarrier.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- American Cancer Society Cancer facts and figures 2017. Genes Dev. 2017;21:2525–2538.
-
- Chabner B.A., Roberts T.G. Timeline: chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:65–72. - PubMed
-
- DeVita V.T., Chu E. A history of cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2008;68:8643–8653. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

