Understanding the Role of Lithium Doping in Reducing Nonradiative Loss in Lead Halide Perovskites
- PMID: 30581694
- PMCID: PMC6299680
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201800736
Understanding the Role of Lithium Doping in Reducing Nonradiative Loss in Lead Halide Perovskites
Abstract
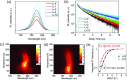
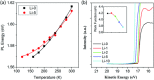
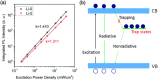
Adding alkali metal into lead halide perovskites has recently been demonstrated as an effective strategy for reducing nonradiative loss. However, the suggested role of the alkali metal is usually limited to surface passivation, and the semiconductor doping effect is rarely discussed. Here, the mechanism of lithium doping in the photocarrier recombination in solution-processed methylammonium lead halide films is investigated by photoluminescence and photoelectron spectroscopies. It is demonstrated that lithium doping weakens the electron-phonon coupling and acts as donor in perovskites, which provide solid evidence that lithium enters the lattice rather than just in the surface region. The n-type doping creates free electrons to fill the trap states in both the bulk and surface regions, leading to suppressed trapping of photocarriers and reduces nonradiative recombination.
Keywords: doping; perovskites; photoluminescence; recombination.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functionalized Substrates for Reduced Nonradiative Recombination in Metal-Halide Perovskites.J Phys Chem Lett. 2025 Jan 9;16(1):372-377. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c03307. Epub 2024 Dec 30. J Phys Chem Lett. 2025. PMID: 39780715 Free PMC article.
-
Giant Light-Emission Enhancement in Lead Halide Perovskites by Surface Oxygen Passivation.Nano Lett. 2018 Nov 14;18(11):6967-6973. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b02887. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Nano Lett. 2018. PMID: 30265549
-
Electrochemical Doping of Halide Perovskites with Ion Intercalation.ACS Nano. 2017 Jan 24;11(1):1073-1079. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b08004. Epub 2017 Jan 10. ACS Nano. 2017. PMID: 28056176
-
The metal doping strategy in all inorganic lead halide perovskites: synthesis, physicochemical properties, and optoelectronic applications.Nanoscale. 2021 Nov 11;13(43):18010-18031. doi: 10.1039/d1nr04706j. Nanoscale. 2021. PMID: 34718363 Review.
-
Defect Passivation in Lead-Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals and Thin Films: Toward Efficient LEDs and Solar Cells.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Sep 27;60(40):21636-21660. doi: 10.1002/anie.202102360. Epub 2021 May 28. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 33730428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Strategy for Tuning Electron-Phonon Coupling and Carrier Cooling in Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Dec 13;13(24):3134. doi: 10.3390/nano13243134. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38133031 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual Temperature Dependence of Bandgap in 2D Inorganic Lead-Halide Perovskite Nanoplatelets.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Oct;8(19):e2100084. doi: 10.1002/advs.202100084. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34382362 Free PMC article.
-
A mechanistic study of the dopant-induced breakdown in halide perovskites using solid state energy storage devices.Energy Environ Sci. 2022 Sep 6;15(10):4323-4337. doi: 10.1039/d2ee01754g. eCollection 2022 Oct 12. Energy Environ Sci. 2022. PMID: 36325485 Free PMC article.
-
Improving photoluminescence properties and reducing recombination of CsPbBr3 perovskite through lithium doping.RSC Adv. 2024 May 8;14(21):15048-15057. doi: 10.1039/d4ra01548g. eCollection 2024 May 2. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38720969 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced coupling of perovskites with semiconductive properties by tuning multi-modal optically active nanostructured set-ups for photonics, photovoltaics and energy applications.RSC Adv. 2025 Feb 25;15(7):5571-5596. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00458f. eCollection 2025 Feb 13. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40007863 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burschka J., Pellet N., Moon S. J., Humphry‐Baker R., Gao P., Nazeeruddin M. K., Grätzel M., Nature 2013, 499, 316. - PubMed
-
- Zhou H., Chen Q., Li G., Luo S., Song T.‐B., Duan H.‐S., Hong Z., You J., Liu Y., Yang Y., Science 2014, 345, 542. - PubMed
-
- Jeon N. J., Noh J. H., Yang W. S., Kim Y. C., Ryu S., Seo J., Seok S. I., Nature 2015, 517, 476. - PubMed
-
- Bi D., Yi C., Luo J., Décoppet J.‐D., Zhang F., Zakeeruddin S. M., Li X., Hagfeldt A., Grätzel M., Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16142. - PubMed
-
- Saliba M., Matsui T., Domanski K., Seo J.‐Y., Ummadisingu A., Zakeeruddin S. M., Correa‐Baena J.‐P., Tress W. R., Abate A., Hagfeldt A., Grätzel M., Science 2016, 354, 206. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
