High-Efficiency, Matrix Interference-Free, General Applicable Probes for Bile Acids Extraction and Detection
- PMID: 30581699
- PMCID: PMC6299822
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201800774
High-Efficiency, Matrix Interference-Free, General Applicable Probes for Bile Acids Extraction and Detection
Abstract
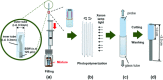
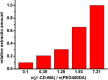
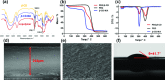
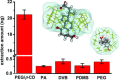
Although bile acids (BAs) have been suggested as important biomarkers for endocrine diseases, the identification and quantification of different BAs are still challenges due to their enormous species and wide range concentrations. Herein, a copolymer probe based on β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) is fabricated through a simple in-mold photopolymerization for the selective extraction of BAs. Through the unique stereochemical affinity between BAs and the cavity of β-CD, the custom probe shows superior enriching capacities to series BAs. Moreover, the outstanding extraction ability is proved to be consistent in various interfering conditions, including pH changing and the addition of complex matrix. Further comparison shows that the stereostructure of the nucleus of BAs plays a vital role during the formation of the β-CD/BA complex, indicating the potential for efficient extraction of other BAs, including their structural analogues or some unknown ones. The developed probe is used for solid phase microextraction, and the limits of detection are lower than 0.075 ng mL-1 by coupling to high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass analysis. The results in this study highlight the potential for effective improvement of immediate detection and profiling of BAs in real samples, which will make a tremendous impact in the analytical field or clinical diagnosis.
Keywords: bile acid; host–guest interactions; matrix interference‐free; solid phase microextraction; β‐cyclodextrin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of bile acids in small volume human bile samples via an amino metal-organic framework composite based solid-phase microextraction probe.J Chromatogr A. 2022 Dec 6;1685:463634. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463634. Epub 2022 Nov 1. J Chromatogr A. 2022. PMID: 36345074
-
Development of analytical method for simultaneous determination of five rodent unique bile acids in rat plasma using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015 Oct 1;1002:399-410. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.08.047. Epub 2015 Sep 3. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26363851
-
Quantitative profiling of bile acids in rat bile using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-orbitrap mass spectrometry: Alteration of the bile acid composition with aging.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016 Sep 15;1031:37-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.07.017. Epub 2016 Jul 9. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27450898
-
[Advances in the development of detection techniques for organophosphate ester flame retardants in food].Se Pu. 2020 Dec 8;38(12):1369-1380. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.03026. Se Pu. 2020. PMID: 34213251 Review. Chinese.
-
Detection technologies and metabolic profiling of bile acids: a comprehensive review.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 May 23;17(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0774-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29792192 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fluorinated-Squaramide Covalent Organic Frameworks for High-Performance and Interference-Free Extraction of Synthetic Cannabinoids.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Nov;10(32):e2302925. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302925. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37807813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sarafian M. H., Lewis M. R., Pechlivanis A., Ralphs S., McPhail M. J. W., Patel V. C., Dumas M., Holmes E., Nicholson J. K., Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9662. - PubMed
-
- Sharma R., Long A., Gilmer J. F., Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4029. - PubMed
-
- Thomas C., Pellicciari R., Pruzanski M., Auwerx J., Schoonjans K., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2008, 7, 678. - PubMed
-
- Baptissart M., Vega A., Maqdasy S., Caira F., Baron S., Lobaccaro J. M. A., Volle D. H., Biochimie 2013, 95, 504. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
