Metabolic treatment of syndrome linked with Parkinson's disease and hypothalamus pituitary gonadal hormones by turmeric curcumin in Bisphenol-A induced neuro-testicular dysfunction of wistar rat
- PMID: 30582014
- PMCID: PMC6296165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2018.12.004
Metabolic treatment of syndrome linked with Parkinson's disease and hypothalamus pituitary gonadal hormones by turmeric curcumin in Bisphenol-A induced neuro-testicular dysfunction of wistar rat
Abstract
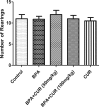
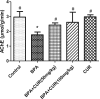
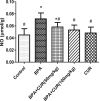
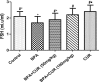
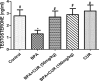
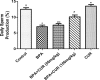
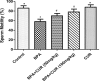
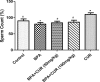
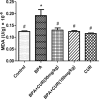
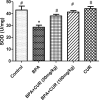
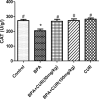
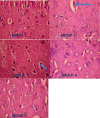
The metabolic shift in cholinesterase activity and inhibitor of hypothalamus pituitary gonadal hormones were hypothesized as resultant effect of Parkinson's disease (PD) which is clinically characterized by a movement disorder. This study therefore examined the effect of turmeric curcumin (CUR) on index of PD, acetylcholine esterase activity and disorder of hypothalamus pituitary gonadal hormone (HPGH) in Bisphenol-A induced injury using animal model. Forty adult male albino rats were randomly distributed into five (n = 8) groups. Group I: vehicle control (olive oil 0.5 ml), Group II was given 50 mg/kg of BPA only, Group III was given 50 mg/kg BPA + 50 mg/kg curcumin, Group IV was given 50 mg/kg BPA + 100 mg/kg curcumin and Group V was administered 50 mg/kg of curcumin only for 14 days. The study examined the effect of curcumin on acetylcholineesterase (AChE) activity, nitric oxide radical (NO•) production, HPGH (LH, FSH and testosterone), MDA level, antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT), in BPA induced male rat. Sperm parameters were similarly examined. The animals induced with BPA exhibited impairment to striatum, leydig cells and sertoli cells by depleting LH, FSH, testosterone and spermatozoa with reduced AChE activity and significant (p < 0.05) alteration in cerebral enzymatic antioxidants. Locomotive activity was impeded followed by the increase of brain NO• level (marker of pro-inflammation). Therapeutically, CUR promoted hypothalamus-pituitary-testicular hormones via modulation of AChE and locomotive activities, reduction of intracellular NO• level, prevention of striatum-endocrine injury as well as oxidative damage. Hence, CUR abolished HPGH dysfunction linked with PD mediated by BPA in rat.
Keywords: Bisphenol-A; Curcumin; Hypothalamus–pituitary–gonadal hormones; Parkinson's disease, rat model.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Biogenic zinc-oxide nanoparticles of Moringa oleifera leaves abrogates rotenone induced neuroendocrine toxicity by regulation of oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase activity.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Apr 17;26:100999. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.100999. eCollection 2021 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 33948501 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic exposure of adult male Wistar rats to bisphenol A causes testicular oxidative stress: Role of gallic acid.Endocr Regul. 2020 Jan 1;54(1):14-21. doi: 10.2478/enr-2020-0003. Endocr Regul. 2020. PMID: 32597147
-
Adult exposure to bisphenol A (BPA) in Wistar rats reduces sperm quality with disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis.Toxicology. 2015 Mar 2;329:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Toxicology. 2015. PMID: 25575453
-
Testicular toxicity of orally administrated bisphenol A in rats and protective role of taurine and curcumin.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019 May;32(3):1043-1047. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 31278718
-
Fighting Bisphenol A-Induced Male Infertility: The Power of Antioxidants.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 15;10(2):289. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020289. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Protective and Therapeutic Anti-Alzheimer Potential of Olea europaea L. cv. Picual: An In Silico and In Vivo Study.Metabolites. 2022 Nov 25;12(12):1178. doi: 10.3390/metabo12121178. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36557216 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects of astragaloside IV and Astragalus spinosus saponins against bisphenol A-induced neurotoxicity and DNA damage in rats.PeerJ. 2021 Aug 9;9:e11930. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11930. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34434659 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge Gap in Understanding the Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Regulation in Steroidogenesis Following Exposure to Bisphenol A and Its Analogues.Biomedicines. 2022 May 30;10(6):1281. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061281. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Protective Effects of Naringin on Oculo-Pulmonary Injury Induced by PM10 (Wood Smoke) Exposure by Modulation of Oxidative Damage and Acetylcholine Esterase Activity in a Rat Model.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2020 Apr 20;92:100586. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2020.100586. eCollection 2020. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2020. PMID: 32419878 Free PMC article.
-
Bisphenol A and Its Analogues Deteriorate the Hormones Physiological Function of the Male Reproductive System: A Mini-Review.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 22;9(11):1744. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111744. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829973 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vandenberg L.N., Hauser R., Marcus M., Olea N., Welshons W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA) Reprod. Toxicol. 2007;24:139–177. - PubMed
-
- Sugiura-Ogasawara M., Ozaki Y., Sonta S., Makino T., Suzumori K. Exposure to bisphenol- A is associated with recurrent miscarriage. Hum. Reprod. 2005;20:2325. - PubMed
-
- Zoeller R.T., Bansal R., Parris C. Bisphenol-A, an environmental contaminant that acts as a thyroid hormone receptor antagonist in vitro, increases serum thyroxine, and alters RC3/neurogranin expression in the developing rat brain. Endocrinology. 2005;146:607. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

