Isolation of allithiamine from Hungarian red sweet pepper seed (Capsicum annuum L.)
- PMID: 30582034
- PMCID: PMC6288420
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00997
Isolation of allithiamine from Hungarian red sweet pepper seed (Capsicum annuum L.)
Abstract
A natural fat-soluble thiamine derivative, namely N-[(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-N-[(2E)-5-hydroxy-3-(prop-2-en-1-yldisulfanyl)pent-2-en-2-yl]formamide (allithiamine) has been identified only in garlic (Allium sativum) until now. Hungarian red sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum) was found as a new source of allithiamine. Extraction procedure and analytical method were developed for the isolation of allithiamine and a chemical synthesis of the compound was also developed. First solid-liquid extraction was performed with 96 % ethanol to isolate allithiamine from pepper seeds. Thereafter, solid phase extraction was applied from ethanolic extract using C18 cartridge to concentrate and purify samples for further analysis. The structure of the synthesized and the isolated compounds was verified by reverse phase HPLC, HPLC-MS, MALD-TOF MS and NMR. Furthermore, effect of allithiamine was investigated on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice with neuropathy. The results show that neuropathic pain sensation is improved by allithiamine treatment similarly to benfothiamine.
Keywords: Analytical chemistry; Food science.
Figures
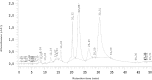

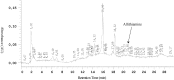





References
-
- Balakumar P., Rohilla A., Krishan P., Solairaj P., Thangathirupathi A. The multifaceted therapeutic potential of benfotiamine. Pharmacol. Res. 2010;61:482–488. - PubMed
-
- Berrone E., Beltramo E., Solimine C., Ape A.U., Porta M. Regulation of intracellular glucose and polyol pathway by thiamine and benfotiamine in vascular cells cultured in high glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:9307–9313. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 2005;54:1615–1625. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

