Atrial-Specific Gene Delivery Using an Adeno-Associated Viral Vector
- PMID: 30582449
- PMCID: PMC6336523
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313811
Atrial-Specific Gene Delivery Using an Adeno-Associated Viral Vector
Abstract
Rationale: Somatic overexpression in mice using an adeno-associated virus (AAV) as gene transfer vectors has become a valuable tool to analyze the roles of specific genes in cardiac diseases. The lack of atrial-specific AAV vector has been a major obstacle for studies into the pathogenesis of atrial diseases. Moreover, gene therapy studies for atrial fibrillation would benefit from atrial-specific vectors. Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) promoter drives gene expression specifically in atrial cardiomyocytes.
Objective: To establish the platform of atrial specific in vivo gene delivery by AAV-ANF.
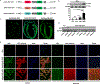
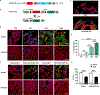
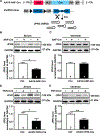
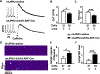
Methods and results: We constructed AAV vectors based on serotype 9 (AAV9) that are driven by the atrial-specific ANF promoter. Hearts from mice injected with AAV9-ANF-GFP (green fluorescent protein) exhibited strong and atrial-specific GFP expression without notable GFP in ventricular tissue. In contrast, similar vectors containing a cardiac troponin T promoter (AAV9-TNT4-GFP) showed GFP expression in all 4 chambers of the heart, while AAV9 with an enhanced chicken β-actin promoter (AAV-enCB-GFP) caused ubiquitous GFP expression. Next, we used Rosa26mT/mG (membrane-targeted tandem dimer Tomato/membrane-targeted GFP), a double-fluorescent Cre reporter mouse that expresses membrane-targeted tandem dimer Tomato before Cre-mediated excision, and membrane-targeted GFP after excision. AAV9-ANF-Cre led to highly efficient LoxP recombination in membrane-targeted tandem dimer Tomato/membrane-targeted green fluorescent protein mice with high specificity for the atria. We measured the frequency of transduced cardiomyocytes in atria by detecting Cre-dependent GFP expression from the Rosa26mT/mG allele. AAV9 dose was positively correlated with the number of GFP-positive atrial cardiomyocytes. Finally, we assessed whether the AAV9-ANF-Cre vector could be used to induce atrial-specific gene knockdown in proof-of-principle experiments using conditional JPH2 (junctophilin-2) knockdown mice. Four weeks after AAV9-ANF-Cre injection, a strong reduction in atrial expression of JPH2 protein was observed. Furthermore, there was evidence for abnormal Ca2+ handling in atrial myocytes isolated from mice with atrial-restricted JPH2 deficiency.
Conclusions: AAV9-ANF vectors produce efficient, dose-dependent, and atrial-specific gene expression following a single-dose systemic delivery in mice. This vector is a novel reagent for both mechanistic and gene therapy studies on atrial diseases.
Keywords: animals; atrial fibrillation; atrial natriuretic factor; gene therapy; mice.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES
XHTW is a founding partner of Elex Biotech, a start-up company that developed drug molecules that target ryanodine receptors for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmia disorders. Other authors have no conflicts.
Figures
Comment in
-
Atrial-Specific Gene Transfer.Circ Res. 2019 Jan 18;124(2):180-182. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314394. Circ Res. 2019. PMID: 30653436 No abstract available.
References
-
- Heeringa J, van der Kuip DA, Hofman A, Kors JA, van Herpen G, Stricker BH, Stijnen T, Lip GY, Witteman JC. Prevalence, incidence and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation: The rotterdam study. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:949–953. - PubMed
-
- Nieuwlaat R, Prins MH, Le Heuzey JY, Vardas PE, Aliot E, Santini M, Cobbe SM, Widdershoven JW, Baur LH, Levy S, Crijns HJ. Prognosis, disease progression, and treatment of atrial fibrillation patients during 1 year: Follow-up of the euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. European heart journal. 2008;29:1181–1189. - PubMed
-
- Shimura D, Kusakari Y, Sasano T, Nakashima Y, Nakai G, Jiao Q, Jin M, Yokota T, Ishikawa Y, Nakano A, Goda N, Minamisawa S. Heterozygous deletion of sarcolipin maintains normal cardiac function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016;310:H92–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

