Novel Hepatitis B Virus Capsid-Targeting Antiviral That Aggregates Core Particles and Inhibits Nuclear Entry of Viral Cores
- PMID: 30582687
- PMCID: PMC6510658
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.8b00235
Novel Hepatitis B Virus Capsid-Targeting Antiviral That Aggregates Core Particles and Inhibits Nuclear Entry of Viral Cores
Abstract
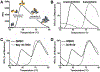
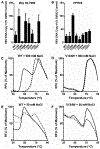
An estimated 240 million are chronically infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV), which can lead to liver disease, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Currently, HBV treatment options include only nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors and the immunomodulatory agent interferon alpha, and these treatments are generally not curative. New treatments with novel mechanisms of action, therefore, are highly desired for HBV therapy. The viral core protein (Cp) has gained attention as a possible therapeutic target because of its vital roles in the HBV life cycle. Several classes of capsid assembly effectors (CAEs) have been described in detail, and these compounds all increase capsid assembly rate but inhibit HBV replication by different mechanisms. In this study, we have developed a thermal shift-based screening method for CAE discovery and characterization, filling a much-needed gap in high-throughput screening methods for capsid-targeting molecules. Using this approach followed by cell-based screening, we identified the compound HF9C6 as a CAE with low micromolar potency against HBV replication. HF9C6 caused large multicapsid aggregates when capsids were assembled in vitro and analyzed by transmission electron microscopy. Interestingly, when HBV-expressing cells were treated with HF9C6, Cp was excluded from cell nuclei, suggesting that this compound may inhibit nuclear entry of Cp and capsids. Furthermore, mutational scanning of Cp suggested that HF9C6 binds the known CAE binding pocket, indicating that key Cp-compound interactions within this pocket have a role in determining the CAE mechanism of action.
Keywords: antiviral; capsid; hepatitis B virus.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Heteroaryldihydropyrimidine Bay 38-7690 Induces Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein Aggregates Associated with Promyelocytic Leukemia Nuclear Bodies in Infected Cells.mSphere. 2018 Apr 18;3(2):e00131-18. doi: 10.1128/mSphereDirect.00131-18. Print 2018 Apr 25. mSphere. 2018. PMID: 29669885 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Characterization of NVR 3-778, a First-in-Class Capsid Assembly Modulator against Hepatitis B Virus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Dec 21;63(1):e01734-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01734-18. Print 2019 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30373799 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a novel hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA encapsidation inhibitor.Antiviral Res. 2020 Mar;175:104709. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104709. Epub 2020 Jan 12. Antiviral Res. 2020. PMID: 31940474
-
Targeting the multifunctional HBV core protein as a potential cure for chronic hepatitis B.Antiviral Res. 2020 Oct;182:104917. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104917. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Antiviral Res. 2020. PMID: 32818519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host functions used by hepatitis B virus to complete its life cycle: Implications for developing host-targeting agents to treat chronic hepatitis B.Antiviral Res. 2018 Oct;158:185-198. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.08.014. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 30145242 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of New Small Molecule Hits as Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators: Structure and Pharmacophore-Based Approaches.Viruses. 2021 Apr 27;13(5):770. doi: 10.3390/v13050770. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33925540 Free PMC article.
-
Current Progress in the Development of Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators: Chemical Structure, Mode-of-Action and Efficacy.Molecules. 2021 Dec 7;26(24):7420. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247420. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34946502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-Aminothiophene-2,4-dicarboxamide analogues as hepatitis B virus capsid assembly effectors.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Feb 15;164:179-192. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.12.047. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30594676 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B Core Protein Capsids.Subcell Biochem. 2021;96:451-470. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58971-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33252740 Review.
-
Structure-Based Discovery of N-Sulfonylpiperidine-3-Carboxamides as Novel Capsid Assembly Modulators for Potent Inhibition of HBV Replication.Viruses. 2022 Feb 8;14(2):348. doi: 10.3390/v14020348. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang L, Zou ZQ, Liu CX, and Liu XZ (2014) Immunotherapeutic interventions in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A review. Journal of immunological methods 407C, 1–8 - PubMed
-
- Lai CL, and Yuen MF (2008) Chronic hepatitis B--new goals, new treatment. The New England journal of medicine 359, 2488–2491 - PubMed
-
- Dienstag JL (2008) Hepatitis B virus infection. The New England journal of medicine 359, 1486–1500 - PubMed
-
- Cox N, and Tillmann H (2011) Emerging pipeline drugs for hepatitis B infection. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 16, 713–729 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

