[A numerical analysis of the effects of the lower-limb prosthetic socket on muscle atrophy of the residual limb]
- PMID: 30583313
- PMCID: PMC9935188
- DOI: 10.7507/1001-5515.201803060
[A numerical analysis of the effects of the lower-limb prosthetic socket on muscle atrophy of the residual limb]
Abstract
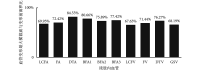
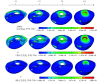
Muscle atrophy of the residual limb after lower-limb amputation is a disadvantage of amputees' rehabilitation. To investigate the biomechanics mechanism of muscle atrophy of the residual limb, we built a finite element model of a residual limb including muscle, skeletons and main vessels based on magnetic resonance images of a trans-femoral amputee, and studied the biomechanics effects of the socket of the lower-limb prosthesis on the soft tissue and vessels in the residual limb. It was found that the descending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex artery suffered the most serious constriction due to the extrusion, while that of the deep femoral artery was comparatively light. Besides, the degree of the constriction of the descending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex vein, femoral vein and deep femoral vein decreased in turn, and that of the great saphenous vein was serious. The stress-strain in the anterior femoral muscle group were highest, while the stress concentration of the inferior muscle group was observed at the end of the thighbone, and other biomechanical indicators at the inferior region were also high. This study validated that the extrusion of the socket on the vessels could cause muscle atrophy to some degree, and provided theoretical references for learning the mechanism of muscle atrophy in residual limb and its effective preventive measures.
下肢截肢后残肢的肌肉萎缩对患者康复十分不利。为探明残肢肌肉萎缩的生物力学机制,本研究利用大腿截肢患者残肢的磁共振断层影像(MRI),建立了包含肌肉、骨骼以及主要血管的残肢有限元模型,研究分析了下肢假肢接受腔对残肢软组织及血管的生物力学影响。结果发现,旋股外侧动脉降支因挤压而发生的狭窄最为严重,股深动脉的狭窄则相对较小;旋股外侧静脉的降支、股静脉、股深静脉狭窄的程度依次降低,大隐静脉的狭窄程度较为严重。前侧肌群中应力应变最高;下侧肌群在股骨的末端处出现应力集中,并且其他生物力学指标在下侧区域中也相对较高。本研究在一定程度上揭示了接受腔对血管的挤压是导致肌肉萎缩的重要原因,这为进一步研究残肢肌肉的萎缩机制和采取有效的预防措施提供了理论参考。.
Keywords: finite element model; muscle atrophy; residual limb; socket; vessel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of arterial flow on muscle atrophy].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Feb 25;36(1):68-72. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201801032. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30887778 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Influence of the scale reduction in designing sockets for trans-tibial amputees.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2020 Aug;234(8):761-768. doi: 10.1177/0954411920921648. Epub 2020 May 30. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2020. PMID: 32475295
-
Internal mechanical conditions in the soft tissues of a residual limb of a trans-tibial amputee.J Biomech. 2008;41(9):1897-909. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2008.03.035. Epub 2008 May 20. J Biomech. 2008. PMID: 18495134
-
Engineering a trans-tibial prosthetic socket for the lower limb amputee.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2011 May;40(5):252-9. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2011. PMID: 21678017 Review.
-
Biomechanical design considerations for transradial prosthetic interface: A review.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2016 Mar;230(3):239-50. doi: 10.1177/0954411915624452. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2016. PMID: 26759485 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources