Environmental Change-Dependent Inherited Epigenetic Response
- PMID: 30583460
- PMCID: PMC6356568
- DOI: 10.3390/genes10010004
Environmental Change-Dependent Inherited Epigenetic Response
Abstract
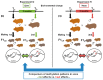
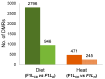
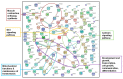
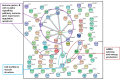
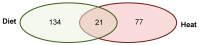
Epigenetic modifications are a mechanism conveying environmental information to subsequent generations via parental germ lines. Research on epigenetic responses to environmental changes in wild mammals has been widely neglected, as well as studies that compare responses to changes in different environmental factors. Here, we focused on the transmission of DNA methylation changes to naive male offspring after paternal exposure to either diet (~40% less protein) or temperature increase (10 °C increased temperature). Because both experiments focused on the liver as the main metabolic and thermoregulation organ, we were able to decipher if epigenetic changes differed in response to different environmental changes. Reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) revealed differentially methylated regions (DMRs) in annotated genomic regions in sons sired before (control) and after the fathers' treatments. We detected both a highly specific epigenetic response dependent on the environmental factor that had changed that was reflected in genes involved in specific metabolic pathways, and a more general response to changes in outer stimuli reflected by epigenetic modifications in a small subset of genes shared between both responses. Our results indicated that fathers prepared their offspring for specific environmental changes by paternally inherited epigenetic modifications, suggesting a strong paternal contribution to adaptive processes.
Keywords: DNA methylation; RRBS; adaptation; exposure; inheritance; plasticity; wild mammal species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diet changes alter paternally inherited epigenetic pattern in male Wild guinea pigs.Environ Epigenet. 2018 Jun 29;4(2):dvy011. doi: 10.1093/eep/dvy011. eCollection 2018 Apr. Environ Epigenet. 2018. PMID: 29992049 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-specific epigenetic inheritance after paternal heat exposure in male wild guinea pigs.Mamm Genome. 2020 Jun;31(5-6):157-169. doi: 10.1007/s00335-020-09832-6. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Mamm Genome. 2020. PMID: 32285146 Free PMC article.
-
Paternal intergenerational epigenetic response to heat exposure in male Wild guinea pigs.Mol Ecol. 2016 Apr;25(8):1729-40. doi: 10.1111/mec.13494. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Mol Ecol. 2016. PMID: 26686986
-
Environmental epigenetic inheritance through gametes and implications for human reproduction.Hum Reprod Update. 2015 Mar-Apr;21(2):194-208. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmu061. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Hum Reprod Update. 2015. PMID: 25416302 Review.
-
Intergenerational Transmission of DNA Methylation Signatures Associated with Early Life Stress.Curr Genomics. 2018 Dec;19(8):665-675. doi: 10.2174/1389202919666171229145656. Curr Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30532646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of gut microbiota in epigenetic regulation of colorectal Cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Jan;1875(1):188490. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188490. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33321173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the past, present and future research landscape of paternal effects.BMC Biol. 2020 Nov 27;18(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12915-020-00892-3. BMC Biol. 2020. PMID: 33246472 Free PMC article.
-
Climate change and epigenetic biomarkers in allergic and airway diseases.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 Nov;152(5):1060-1072. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.09.011. Epub 2023 Sep 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37741554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics as Driver of Adaptation and Diversification in Microbial Eukaryotes.Front Genet. 2021 Mar 16;12:642220. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.642220. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33796133 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
MicroRNAs and Epigenetics Strategies to Reverse Breast Cancer.Cells. 2019 Oct 8;8(10):1214. doi: 10.3390/cells8101214. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31597272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- West-Eberhard M.J. Phenotypic plasticity and the origins of diversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1989;20:249–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.20.110189.001341. - DOI
-
- Stearns S.C. The Evolution of Life Histories. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 1992. 249p
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

