Dispensing of Prescribed Medicines in Swiss Community Pharmacies-Observed Counselling Activities
- PMID: 30583485
- PMCID: PMC6473540
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmacy7010001
Dispensing of Prescribed Medicines in Swiss Community Pharmacies-Observed Counselling Activities
Abstract
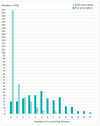
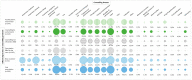
Patient counselling and addressing drug-related problems are the pharmacist's key activities to ensure the safe and effective use of medicines. This study aimed to describe the dispensing practice of prescribed medicines in daily community pharmacy practice and to identify factors influencing counselling provision; Methods: An observational study was conducted in community pharmacies in Basel, Switzerland. One master student in pharmacy performed non-participatory observations for one day at each of the participating community pharmacies. Patient characteristics, counselling content, additional activities, and pharmaceutical interventions were documented on a structured checklist; Results: 556 prescription encounters (PE) in 18 participating community pharmacies were observed (269 first prescriptions; 287 refill prescriptions). Patients were regular customers (n = 523, 94.1%) and 53.8 ± 23.4 years old. Counselling was provided to 367 (66.0%) customers on 2.9 ± 3.1 themes per PE. Factors influencing counselling were dispensing by the pharmacist, new customer, customer who did not refuse counselling, customer with a first prescription, with a prescription resulting in a pharmaceutical intervention, and a prescription filled by carers. During 144 PEs, 203 interventions were documented. Pharmacists proposed few additional activities and performed no cognitive pharmaceutical service; Conclusions: Our study quantified counselling and additional services at the dispensing of prescribed medicines and identified influencing factors on counselling provision at the patient, prescription, and pharmacy level.
Keywords: community pharmacy practice; counselling; dispensing; observation; pharmaceutical care; pharmaceutical intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Spivey P. MDS-3: Managing Access to Medicines and Health Technologies. Management Sciences for Health; Arlington, VA, USA: 2012. Ensuring good dispensing practices.
-
- World Health Organization, editor. Joint FIP/WHO Guidelines on Good Pharmacy Practice: Standards for Quality of Pharmacy Services. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2011. [(accessed on 27 August 2018)]. (WHO Technical Report Series). Available online: https://www.fip.org/www/uploads/database_file.php?id=331&table_id=
-
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists ASHP guidelines on pharmacist-conducted patient education and counselling. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 1997;54:431–434. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

