Molecules that Inhibit Bacterial Resistance Enzymes
- PMID: 30583527
- PMCID: PMC6337270
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24010043
Molecules that Inhibit Bacterial Resistance Enzymes
Abstract
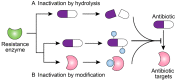
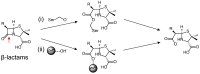
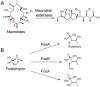
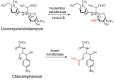
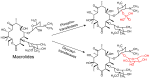
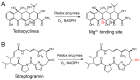
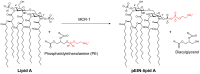
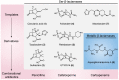
Antibiotic resistance mediated by bacterial enzymes constitutes an unmet clinical challenge for public health, particularly for those currently used antibiotics that are recognized as "last-resort" defense against multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. Inhibitors of resistance enzymes offer an alternative strategy to counter this threat. The combination of inhibitors and antibiotics could effectively prolong the lifespan of clinically relevant antibiotics and minimize the impact and emergence of resistance. In this review, we first provide a brief overview of antibiotic resistance mechanism by bacterial secreted enzymes. Furthermore, we summarize the potential inhibitors that sabotage these resistance pathways and restore the bactericidal activity of inactive antibiotics. Finally, the faced challenges and an outlook for the development of more effective and safer resistance enzyme inhibitors are discussed.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; bacterial enzymes; molecules; therapeutic potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bacterial fatty acid metabolism in modern antibiotic discovery.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 Nov;1862(11):1300-1309. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.09.014. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 27668701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiotic adjuvants - A strategy to unlock bacterial resistance to antibiotics.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Sep 15;27(18):4221-4228. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.08.027. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 28827113 Review.
-
Novel Antibacterial Targets in Protein Biogenesis Pathways.Chembiochem. 2022 Feb 16;23(4):e202100459. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100459. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 34643994 Review.
-
Targeting bacterial topoisomerases: how to counter mechanisms of resistance.Future Med Chem. 2016 Jun;8(10):1085-100. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2016-0042. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Future Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27285067 Review.
-
Targeting the Bacterial Transglycosylase: Antibiotic Development from a Structural Perspective.ACS Infect Dis. 2019 Sep 13;5(9):1493-1504. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00118. Epub 2019 Jul 8. ACS Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31283163 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic analysis of Staphylococcus equorum KM1031 from the high-salt fermented seafood jeotgal under chloramphenicol, erythromycin and lincomycin stresses.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 15;12(1):15541. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19897-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36109627 Free PMC article.
-
The Promising Potential of Reverse Vaccinology-Based Next-Generation Vaccine Development over Conventional Vaccines against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jul 20;11(7):1264. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11071264. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37515079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention and potential remedies for antibiotic resistance: current research and future prospects.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 3;15:1455759. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1455759. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39421555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Ω-Loop in Regulation of the Catalytic Activity of TEM-Type β-Lactamases.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 11;9(12):854. doi: 10.3390/biom9120854. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31835662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Weakest-Link Dynamics Predict Apparent Antibiotic Interactions in a Model Cross-Feeding Community.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Oct 20;64(11):e00465-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00465-20. Print 2020 Oct 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32778550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CDC Threat Report: ‘We Will Soon Be in a Post-Antibiotic Era’. [(accessed on 22 December 2018)]; Available online: https://www.wired.com/2013/09/cdc-amr-rpt1/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

