Analysis of Polymorphism and Expression Profile of ASIC1 and IL-6 Genes in Patients with Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 30583668
- PMCID: PMC6428554
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.12.3451
Analysis of Polymorphism and Expression Profile of ASIC1 and IL-6 Genes in Patients with Gastric Cancer
Abstract
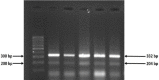
Gastric cancer is one of the most common upper gastrointestinal malignancies. Some Iranian provinces, such as in the northern and northwestern areas, are at a high risk, whereas the central and western provinces are at a medium and the southern regions at low risk. This study was carried out to estimate the impact of the expression patterns of ASIC1 and IL-6 genes and the IL-6rs-174 and ASIC1rs 75624685 polymorphisms in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Materials and methods: Tetra-ARMS PCR was employed to analyze the polymorphism status of the ASIC1 and IL-6 genes with 85 paraffin-embedded tissue blocks from cases and 117 normal blood samples as controls. We also investigated mRNA expression levels of these genes in 12 cases and controls using real-time PCR. Results: Our results showed a significant association between expression of ASIC1 and elevated risk of gastric cancer (p<0.001).
Keywords: Gastric cancer; polymorphism; expression; IL-6; ASIC1.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures
Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of ASIC1 suppressed gastric cancer via inhibiting autophagy.Gene. 2017 Apr 15;608:79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.01.014. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28111260
-
Polymorphisms in interleukin-6-6331 influences the susceptibility of a Chinese population to gastric cancer.Cancer Invest. 2011 Oct;29(8):564-72. doi: 10.3109/07357907.2011.605411. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Cancer Invest. 2011. PMID: 21843047
-
IL-1B (C+3954T) gene polymorphism and susceptibility to gastric cancer in the Iranian population.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(2):841-4. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.2.841. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25684535
-
Meta-analysis: tumour invasion-related genetic polymorphisms and gastric cancer susceptibility.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Sep 1;28(5):565-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03760.x. Epub 2008 Jun 9. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18544073 Review.
-
Polymorphism of IL-8 in 251 allele and gastric cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis.Dig Dis Sci. 2010 Jul;55(7):1818-23. doi: 10.1007/s10620-009-0978-y. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Dig Dis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19777350 Review.
Cited by
-
Alteration and dysfunction of ion channels/transporters in a hypoxic microenvironment results in the development and progression of gastric cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021 Aug;44(4):739-749. doi: 10.1007/s13402-021-00604-1. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 33856653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiologic Study of Gastric Cancer in Iran: A Systematic Review.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2020 Nov 5;13:511-542. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S256627. eCollection 2020. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33177859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased expression of interleukin-6 gene in gastritis and gastric cancer.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021 May 17;54(7):e10687. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2020e10687. eCollection 2021. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021. PMID: 34008757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:1–78. - PubMed
-
- Amjadi O, Rafiei A, Ajami A, Hosseini V, Asgarian-Omran H. Inflammation, a key factor in cancer ambush. Res Mol Med. 2014a;2:1–15.
-
- Chen L, Yuan W, Chen Z, et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide represses activation of tumor-associated macrophages in gastric cancer via regulation of TNFα, IL-6, IL-12 and iNOS. Int J Oncol. 2015;47:1361–70. - PubMed
-
- Duch CR, Figueiredo MS, Ribas C, et al. Analysis of polymorphism at site -174 G/C of interleukin-6 promoter region in multiple myeloma. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007;40:265–7. - PubMed
-
- Furukawa K, Takahashi T, Arai F, Matsushima K, Asakura H. Enhanced mucosal expression of interleukin-6 mRNA but not of interleukin-8 mRNA at the margin of gastric ulcer in Helicobacter pylori-positive gastritis. J Gastroenterol. 1998;33:625–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical