Expression of PAX-5 in B Cell Hodgkin and Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
- PMID: 30583670
- PMCID: PMC6428548
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.12.3463
Expression of PAX-5 in B Cell Hodgkin and Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
Abstract
Background: B-cell malignancies including Precursor B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia and Hodgkin Lymphoma show a wide spectrum of B-cell differentiation from early stage B-cell precursors to mature B-cells ending in terminal differentiation to plasma cells. Pan-B-cell antigens routinely used for the diagnosis of B-cell lymphoma, include CD19, CD20, CD22 and CD79a.PAX-5 protein, also known as B-cell-specific activation protein is a B-cell-specific transcription factor; essential for commitment and functional maintenance used in the diagnosis of B cell Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. PAX-5 show nuclear positivity in B cell lymphomas and moderate (dim) positivity in Hodgkinlymphoma Reed Sternberg cells make this marker ideal for diagnosing B cell malignances. Objective: To determine the expression of PAX-5 in B cell Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in order to improve the diagnosis of B-cell lymphomas. Methods: In this Prospective study, all the cases of B cell lymphoma diagnosed at The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi from July 2010 to July 2011were included. A panel of Immunohistochemical stain was performed in all cases along with additional PAX- 5 stain with appropriate controls. Results: Total 125 cases were included. Hodgkin Lymphoma (Mixed cellularity) was the commonest B-cell lymphoma subtype, 32 (25%) cases. Other common subtypes included Hodgkin lymphoma (Nodular sclerosis subtype), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and B lymphoblastic lymphoma. Conclusion: This study demonstrates that PAX-5 is the most sensitive and reliable immuhohistochemicalmarker in the diagnosis of B cell Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Keywords: PAX-5; Hodgkin Lymphoma; Non Hodgkin Lymphoma.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures


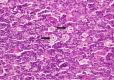

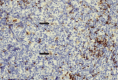
 , which is helpful for histopathologists to identify reed-sternberg cells while background B cell are strongly positive for PAX-5.
, which is helpful for histopathologists to identify reed-sternberg cells while background B cell are strongly positive for PAX-5.Similar articles
-
The value of anti-pax-5 immunostaining in routinely fixed and paraffin-embedded sections: a novel pan pre-B and B-cell marker.Am J Surg Pathol. 2002 Oct;26(10):1343-50. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200210000-00011. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12360049
-
Use of an expanded immunohistochemical panel to distinguish cutaneous Hodgkin lymphoma from histopathologic imitators.J Cutan Pathol. 2012 Jun;39(6):651-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2012.01872.x. Epub 2012 Feb 11. J Cutan Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22324490
-
B-cell transcription factors Pax-5, Oct-2, BOB.1, Bcl-6, and MUM1 are useful markers for the diagnosis of nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011;52(1):69-74. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011. PMID: 21424034
-
Reed-Sternberg-Like Cells in Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015 Oct;139(10):1205-10. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2015-0197-RAI. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015. PMID: 26414463 Review.
-
Diagnostic uses of Pax5 immunohistochemistry.Adv Anat Pathol. 2007 Sep;14(5):323-34. doi: 10.1097/PAP.0b013e3180ca8a49. Adv Anat Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17717432 Review.
Cited by
-
Promising drugs and treatment options for pediatric and adolescent patients with Hodgkin lymphoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 24;10:965803. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.965803. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36506094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of exportins expression unveils their prognostic significance in colon adenocarcinoma: insights from public databases.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jan 8;16(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01748-4. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39776001 Free PMC article.
-
Variable Expression of Notch1 and Pax5 in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Infection with Epstein-Barr in Pediatric Patients.Microorganisms. 2020 Jun 26;8(6):958. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8060958. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32604737 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical expression of transcription factors PAX5, OCT2, BCL6 and transcription regulator P53 in Non-Hodgkin lymphomas: A diagnostic cross-sectional study.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 May 14;78:103786. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103786. eCollection 2022 Jun. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35600178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams B, Dörfler P, Aguzzi A, et al. Pax-5 encodes the transcription factor BSAP and is expressed in B lymphocytes, the developing CNS, and adult testis. Genes Dev. 1992;6:1589–607. - PubMed
-
- Aftab K, Bhurgri Y, Pervez S. Small B cell Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma in Pakistan. J Pak Med Assoc. 2006;56:22–5. - PubMed
-
- Barakzai MA, Pervez S. CD20 positivity in classical Hodgkin's lymphoma:Diagnostic challenge or targeting opportunity. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2009;52:6–9. - PubMed
-
- Buettner M, Greiner A, Avramidou A, Jäck HM, Niedobitek G. Evidence of abortive plasma cell differentiation in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Hematol Oncol. 2005;23:127–32. - PubMed
-
- Chu PG, Loera S, Huang Q, Weiss LM. Lineage determination of CD20- B-Cell neoplasms:an immunohistochemical study. Am J ClinPathol. 2006;126:534–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

