Anticancer Activity of Camel Milk via Induction of Autophagic Death in Human Colorectal and Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 30583676
- PMCID: PMC6428541
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.12.3501
Anticancer Activity of Camel Milk via Induction of Autophagic Death in Human Colorectal and Breast Cancer Cells
Erratum in
-
Anticancer Activity of Camel Milk via Induction of Autophagic Death in Human Colorectal and Breast Cancer Cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018; 19(12): 3501-3509. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.12.3501. Roopesh Krishnankutty et al.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 May 1;21(5):1495. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.5.1495. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32458661 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
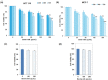
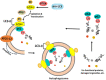
Background/ Objective: Camel milk is traditionally known for its human health benefits and believed to be a remedy for various human ailments including cancer. The study was aimed to evaluate the inhibitory effects of commercially available camel milk on cancer cells and its underlying mechanism(s). Materials and Methods: Two cell lines: colorectal cancer HCT 116 and breast cancer MCF-7 were cultured with different doses of camel milk. The effects of camel milk on cell death were determined by MTT assay, viability by trypan blue exclusion assay and migration by in vitro scratch assay. The mechanism was elucidated by western blotting and confocal microscopy was used to confirm autophagy. Results: Camel milk significantly reduced proliferation, viability as well as migration of both the cells. The accumulation of LC3-II protein along with reduction in expression of p62 and Atg 5-12, the autophagy proteins implied induction of autophagy. The (GFP)-LC3 puncta detected by confocal microscopy confirmed the autophagosome formation in response to camel milk treatment. Conclusion: Camel milk exerted antiproliferative effects on human colorectal HCT 116 and breast MCF-7 cancer cells by inducing autophagy.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; breast cancer; camel milk; autophagy.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures




Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Effect of Camel Milk and Its Exosomes on MCF7 Cells In Vitro and In Vivo.Integr Cancer Ther. 2018 Dec;17(4):1235-1246. doi: 10.1177/1534735418786000. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Integr Cancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 29986606 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagic flux disruption contributes to Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells via MAPK/ERK activation.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jun 11;10(6):456. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1653-7. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31186406 Free PMC article.
-
Evodiamine exerts anticancer effects via induction of apoptosis and autophagy and suppresses the migration and invasion of human colon cancer cells.J BUON. 2019 Sep-Oct;24(5):1824-1829. J BUON. 2019. PMID: 31786843
-
Small Molecules Targeting Programmed Cell Death in Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 8;22(18):9722. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189722. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Characterizing Natural Products that Regulate Autophagy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(18):2177-2196. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666191015104458. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31749434 Review.
Cited by
-
Facile Synthesis of Multifunctional Carbon Dots Derived from Camel Milk for Mn7+ Sensing and Antiamyloid and Anticancer Activities.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 20;8(39):36521-36533. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05485. eCollection 2023 Oct 3. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37810638 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of probiotic camel milk as a nutritional beverage: Challenges and perspectives.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Jun 24;12(9):6123-6141. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4298. eCollection 2024 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39554333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of camel milk lactoferrin peptides against breast cancer cells: in silico and in vitro study.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 19;15:1425504. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1425504. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39629082 Free PMC article.
-
Development and clinical validation of a novel platelet count-based nomogram for predicting microvascular invasion in HCC.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 18;15(1):5881. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88343-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39966444 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the genomic resources of seven domestic Bactrian camel populations in China through restriction site-associated DNA sequencing.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 29;16(4):e0250168. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250168. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33914766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal RP, Dogra R, Mohta N, et al. Beneficial effect of camel milk in diabetic nephropathy. Acta Biomedica. 2009;80:131–4. - PubMed
-
- Al-Kuraya K, Schraml P, Sheikh S, et al. Predominance of high-grade pathway in breast cancer development of Middle East women. Mod Pathol. 2005;18:891–7. - PubMed
-
- Alebie G, Yohannes S, Worku A. Therapeutic applications of camel's milk and urine against cancer:current development efforts and future perspectives. J Cancer Sci Ther. 2017;9:468–78.
-
- Alhaider AA, Abdel Gader AG, Almeshaal N, et al. Camel milk inhibits inflammatory angiogenesis via downregulation of proangiogenic and proinflammatory cytokines in mice. Acta Pathologica Microbiologica Et Immunonologica Scandinavica. 2014;122:599–607. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

