Automatic Approach for Cervical Cancer Detection and Segmentation Using Neural Network Classifier
- PMID: 30583685
- PMCID: PMC6428557
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.12.3571
Automatic Approach for Cervical Cancer Detection and Segmentation Using Neural Network Classifier
Abstract
Cervical cancer leads to major death disease in women around the world every year. This cancer can be cured if it is initially screened and giving timely treatment to the patients. This paper proposes a novel methodology for screening the cervical cancer using cervigram images. Oriented Local Histogram Technique (OLHT) is applied on the cervical image to enhance the edges and then Dual Tree Complex Wavelet Transform (DT-CWT) is applied on it to obtain multi resolution image. Then, features as wavelet, Grey Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM), moment invariant and Local Binary Pattern (LBP) features are extracted from this transformed multi resolution cervical image. These extracted features are trained and also tested by feed forward back propagation neural network to classify the given cervical image into normal and abnormal. The morphological operations are applied on the abnormal cervical image to detect and segment the cancer region. The performance of the proposed cervical cancer detection system is analyzed in the terms of sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, Likelihood Ratio positive, Likelihood ratio negative, precision, false positive rate and false negative rate. The performance measures for the cervical cancer detection system achieves 97.42% of sensitivity, 99.36% of specificity, 98.29% of accuracy, PPV of 97.28%, NPV of 92.17%, LRP of 141.71, LRN of 0.0936, 97.38 % precision, 96.72% FPR and 91.36% NPR. From the simulation results, the proposed methodology outperforms the conventional methodologies for cervical cancer detection and segmentation process.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; cervigram; features; Gabor transforms; neural networks.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures
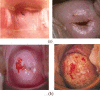


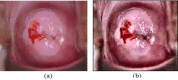




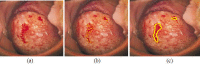
References
-
- American Cancer Society (ACS) What is cervical Cancer? 2011. Available at:< http://www.Cancer.org/Cancer/CervicalCancer/Detailed-Guide/cervical-Canc... .
-
- Bergmeir C, Silvente MG, Benitez JM. Segmentation of cervical cell nuclei in high-resolution microscopic images:a new algorithm and a web-based software framework. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2012;107:497–512. - PubMed
-
- Chen YF, Huang PC, Lin KC, et al. Semi-automatic segmentation and classification of pap smear cells. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2014;18:1. - PubMed
-
- Demir C, Yener B. Automated cancer diagnosis based on histopathological images:a systematic survey, Tech. New York, NY, USA: Rep., Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute; 2005.
-
- Devi MA, Ravi S, Vaishnavi J, Punitha S. Classification of cervical cancer using artificial neural networks. Procedia Comput Sci. 2016;89:465–72.

