The role of the ERK1/2 pathway in simvastatin-loaded nanomicelles and simvastatin in regulating the osteogenic effect in MG63 cells
- PMID: 30584296
- PMCID: PMC6287536
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S182998
The role of the ERK1/2 pathway in simvastatin-loaded nanomicelles and simvastatin in regulating the osteogenic effect in MG63 cells
Abstract
Objectives: The present study aimed to clarify the role of the ERK1/2 pathway in simvastatin (SV)-loaded nanomicelles (SVNs)- and SV-mediated promotion of cell osteogenic differentiation and explore the molecular mechanisms by which SVNs exhibited a greater efficacy in promoting osteogenic differentiation than SV.
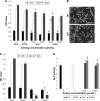
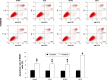
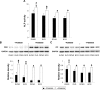
Materials and methods: SVNs were synthesized using a dialysis method. MG63 cells were treated with 2.5, 0.25, and 0.025 μmol/L of the drug. The optimal drug dosage was determined by examining the proliferative activity and ALP activity of the MG63 cells. Subsequently, Western blot analysis was performed to analyze the levels of the phosphorylated ERK1/2 proteins in each experimental group at various time points. Finally, the inhibitor PD98059 was used to effectively inhibit the ERK1/2 pathway. The resulting changes in the proliferative activity of MG63 cells and the osteogenesis-related markers were analyzed.
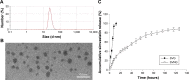
Results: The SVNs synthesized in the present study had a mean diameter of 27 nm. The encapsulation and drug-loading efficiencies were 52.03% ± 4.05% and 9.42% ± 0.66%, respectively. SVNs and SV exhibited optimum osteogenesis-promoting effects when the drugs were administered at a concentration of 0.25 μmol/L. The drug-induced activation of the ERK1/2 pathway reached a peak at 15 minutes after administration and then declined rapidly. From 24 hours to 7 days, SVNs and SV exerted an inhibitory effect on the ERK1/2 pathway rather than an activating effect. Throughout the whole experimental process, the regulatory effect of SVNs on the ERK1/2 pathway was significantly greater than that of SV. Inhibition of the ERK1/2 pathway by PD98059 markedly reduced the proliferative activity of the cells in all experimental groups. In addition, the ALP activity and the expression levels of the osterix (OSX) and osteocalcin (OC) proteins were drastically increased.
Conclusion: SVNs significantly increased the effect of SV-induced osteogenic differentiation by strongly inhibiting the ERK1/2 pathway.
Keywords: ERK1/2 pathway; dental implant restoration; osteogenic effect; simvastatin-loaded nanomicelles.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The roles of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway in regulating osteogenic differentiation of murine preosteoblasts MC3T3-E1 cells on roughened titanium surfaces.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012 Jan;100(1):125-33. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.33247. Epub 2011 Oct 14. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012. PMID: 21997903
-
[REGUL ATORY EFFECT OF SIMVASTATIN ON MIDDLE/L ATE STAGES OSTEOGENIC DIFFERENTIATION OF BONE MARROW MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS VIA p38MAPK PATHWAY].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Aug 8;30(8):1038-1043. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.20160208. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 29786238 Chinese.
-
Nell-1 Enhances Osteogenic Differentiation of Pre-Osteoblasts on Titanium Surfaces via the MAPK-ERK Signaling Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(4):1522-1534. doi: 10.1159/000494651. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30359975
-
Encapsulation of a nanoporous simvastatin-chitosan composite to enhance osteointegration of hydroxyapatite-coated polyethylene terephthalate ligaments.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jul 4;14:4881-4893. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S210687. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31308664 Free PMC article.
-
An in vitro study of a titanium surface modified by simvastatin-loaded titania nanotubes-micelles.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014 Feb;10(2):194-204. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2014.1810. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24738328
Cited by
-
Functional identification of a rare vascular endothelial growth factor a (VEGFA) variant associating with the nonsyndromic cleft lip with/without cleft palate.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):1471-1483. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1912547. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 33947308 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Simvastatin-Loaded Nanomicelles on the Early Preservation of Tooth Extraction Sites.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Oct 1;19:10065-10076. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S481498. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39371480 Free PMC article.
-
Arylated gold nanoparticles have no effect on the adipogenic differentiation of MG-63 cells nor regulate any key signaling pathway during the differentiation.BMC Res Notes. 2021 May 19;14(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s13104-021-05594-9. BMC Res Notes. 2021. PMID: 34011402 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances on small molecules in osteogenic differentiation of stem cells and the underlying signaling pathways.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Nov 12;13(1):518. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03204-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36371202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Nawas B, Schiegnitz E. Augmentation procedures using bone substitute materials or autogenous bone – a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2014;7(Suppl 2):S219–S234. - PubMed
-
- Mundy G, Garrett R, Harris S, et al. Stimulation of bone formation in vitro and in rodents by statins. Science. 1999;286(5446):1946–1949. - PubMed
-
- Allon I, Anavi Y, Allon DM. Topical simvastatin improves the pro-angiogenic and pro-osteogenic properties of bioglass putty in the rat calvaria critical-size model. J Oral Implantol. 2014;40(3):251–258. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

