The Portuguese Severe Asthma Registry: Development, Features, and Data Sharing Policies
- PMID: 30584531
- PMCID: PMC6280304
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1495039
The Portuguese Severe Asthma Registry: Development, Features, and Data Sharing Policies
Abstract
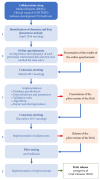
The Portuguese Severe Asthma Registry (Registo de Asma Grave Portugal, RAG) was developed by an open collaborative network of asthma specialists. RAG collects data from adults and pediatric severe asthma patients that despite treatment optimization and adequate management of comorbidities require step 4/5 treatment according to GINA recommendations. In this paper, we describe the development and implementation of RAG, its features, and data sharing policies. The contents and structure of RAG were defined in a multistep consensus process. A pilot version was pretested and iteratively improved. The selection of data elements for RAG considered other severe asthma registries, aiming at characterizing the patient's clinical status whilst avoiding overloading the standard workflow of the clinical appointment. Features of RAG include automatic assessment of eligibility, easy data input, and exportable data in natural language that can be pasted directly in patients' electronic health record and security features to enable data sharing (among researchers and with other international databases) without compromising patients' confidentiality. RAG is a national web-based disease registry of severe asthma patients, available at asmagrave.pt. It allows prospective clinical data collection, promotes standardized care and collaborative clinical research, and may contribute to inform evidence-based healthcare policies for severe asthma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Design, development and deployment of a web-based interoperable registry for inherited retinal dystrophies in Portugal: the IRD-PT.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020 Oct 27;15(1):304. doi: 10.1186/s13023-020-01591-6. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020. PMID: 33109251 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps impact in severe asthma patients: Evidences from the Severe Asthma Network Italy (SANI) registry.Respir Med. 2020 May;166:105947. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.105947. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 32250875
-
Characterization of Severe Asthma Worldwide: Data From the International Severe Asthma Registry.Chest. 2020 Apr;157(4):790-804. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.10.053. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Chest. 2020. PMID: 31785254
-
International Severe Asthma Registry: Mission Statement.Chest. 2020 Apr;157(4):805-814. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.10.051. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Chest. 2020. PMID: 31838187 Review.
-
Database and Registry Research in Orthopaedic Surgery: Part I: Claims-Based Data.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015 Aug 5;97(15):1278-87. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.N.01260. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015. PMID: 26246263 Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping Digital Public Health Interventions Among Existing Digital Technologies and Internet-Based Interventions to Maintain and Improve Population Health in Practice: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Jul 17;26:e53927. doi: 10.2196/53927. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39018096 Free PMC article.
-
Blueprint for harmonising unstandardised disease registries to allow federated data analysis: prepare for the future.ERJ Open Res. 2022 Oct 4;8(4):00168-2022. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00168-2022. eCollection 2022 Oct. ERJ Open Res. 2022. PMID: 36199590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult Severe Asthma Registries: A Global and Growing Inventory.Pragmat Obs Res. 2023 Oct 20;14:127-147. doi: 10.2147/POR.S399879. eCollection 2023. Pragmat Obs Res. 2023. PMID: 37881411 Free PMC article.
-
The Korean Severe Asthma Registry (KoSAR): real world research in severe asthma.Korean J Intern Med. 2022 Feb;37(2):249-260. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2021.403. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Korean J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35184515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GEMA 5.3. Spanish Guideline on the Management of Asthma.Open Respir Arch. 2023 Sep 19;5(4):100277. doi: 10.1016/j.opresp.2023.100277. eCollection 2023 Oct-Dec. Open Respir Arch. 2023. PMID: 37886027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GINA. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention (updated 2018). Global Initiative for Asthma. 2018.
-
- Gliklich R. In: Registries for Evaluating Patient Outcomes: A User’s Guide. Dreyer N., Leavy M., editors. Rockville, Md, USA: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2014. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK208616/ - PubMed

