New Molecular Aspects of Cardiac Arrest; Promoting Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Approaches
- PMID: 30584556
- PMCID: PMC6289159
New Molecular Aspects of Cardiac Arrest; Promoting Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Approaches
Abstract
Introduction: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a method to improve survival of patients with cardiac arrest. This study aimed to identify the key genes affected five minutes after cardiac arrest, hoping to elevate the efficacy of CPR.
Methods: In this bioinformatics study differentially expressed genes of six pigs were downloaded from GEO and screened. The significant and characterized genes were analyzed via calculating fold change and protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks. The crucial nodes were determined based on centrality parameters and their related biological processes were investigated via ClueGO.
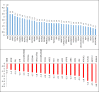
Results: 17 significant up-regulated (LogFC ≥ 2) and 22 down-regulated (LogFC < -0.5) genes were detected. Transthyretin (TTR logFC = 4.59) and Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GNRHR logFC = 3.84) had higher logFC among up-regulated and down-regulated genes, respectively. The critical genes including four up-regulated and five down-regulated genes were detected from network analysis. GNRHR and Prolactin precursor (PRL) were among the most important down res 5 minutes after cardiac arrest and Beta-2 adrenergic receptor and Cadherin-1 were among the most important up regulated gens.
Conclusion: The introduced potential biomarkers could reveal a new molecular aspect for CPR performance and pituitary gland protection was highlighted in this respect.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cardiac Arrest; Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation; Gene Ontology; Protein Interaction Maps.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yeung J, Meeks R, Edelson D, Gao F, Soar J, Perkins GD. The use of CPR feedback/prompt devices during training and CPR performance: a systematic review. Resuscitation. 2009;80(7):743–51. - PubMed
-
- Zhao H, Li C-S, Gong P, Tang Z-R, Hua R, Mei X, et al. Molecular mechanisms of therapeutic hypothermia on neurological function in a swine model of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2012;83(7):913–20. - PubMed
-
- Böttiger BW, Motsch J, Braun V, Martin E, Kirschfink M. Marked activation of complement and leukocytes and an increase in the concentrations of soluble endothelial adhesion molecules during cardiopulmonary resuscitation and early reperfusion after cardiac arrest in humans. Critical care medicine. 2002;30(11):2473–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
