Oral Oxycodone Compared With Intravenous Morphine Sulfate for Pain Management of Isolated Limb Trauma; a Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 30584575
- PMCID: PMC6289158
Oral Oxycodone Compared With Intravenous Morphine Sulfate for Pain Management of Isolated Limb Trauma; a Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Introduction: Appropriate pain relief enhances patient satisfaction and reduces patient anxiety. This study aimed to compare oral oxycodone with intravenous (IV) morphine sulfate (MS) in pain management of acute limb trauma.
Method: In this randomized double-blind clinical trial, patients over 14 years old, with acute isolated limb trauma were randomized to receive either 5mg IV MS or 5 mg oral oxycodone. Pain intensity and adverse effects of medications were recorded 0, 30 and 60 minutes after drug administration and compared between the groups.
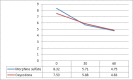
Result: 58 patients were studied. Pain intensity was similar between the two studied groups at 30 minutes (P = 0.834) and 60 minutes (P = 0.880) after drug administration. Furthermore, there was no significant difference between the two groups regarding decrease in pain within the defined time interval. Drowsiness was reported more frequently in MS group after 30 minutes (p = 0.006). Patients in MS group asked for more rescue analgesia. Other adverse effects were similar in both groups.
Conclusion: Oral oxycodone is as effective as IV morphine sulfate in treatment of acute musculoskeletal pain following blunt limb trauma.
Keywords: Oxycodone; acute pain; morphine; wounds and injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this study certify that they have NO involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral versus intravenous opioid dosing for the initial treatment of acute musculoskeletal pain in the emergency department.Acad Emerg Med. 2008 Dec;15(12):1234-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2008.00266.x. Epub 2008 Oct 17. Acad Emerg Med. 2008. PMID: 18945240 Clinical Trial.
-
Analgesic efficacy and tolerability of intravenous morphine versus combined intravenous morphine and oxycodone in a 2-center, randomized, double-blind, pilot trial of patients with moderate to severe pain after total hip replacement.Clin Ther. 2012 Aug;34(8):1751-60. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.06.023. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Clin Ther. 2012. PMID: 22795613 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral oxycodone plus intravenous acetaminophen versus intravenous morphine sulfate in acute bone fracture pain control: a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014 Oct;24(7):1305-9. doi: 10.1007/s00590-013-1392-x. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014. PMID: 24356922 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral Oxycodone for Acute Postoperative Pain: A Review of Clinical Trials.Pain Physician. 2017 Feb;20(2S):SE33-SE52. Pain Physician. 2017. PMID: 28226340 Review.
-
Intravenous Oxycodone Versus Other Intravenous Strong Opioids for Acute Postoperative Pain Control: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.Pain Ther. 2019 Jun;8(1):19-39. doi: 10.1007/s40122-019-0122-4. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Pain Ther. 2019. PMID: 31004317 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of opioids for traumatic pain in the emergency department: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 27;14:1209131. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1209131. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37576822 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the effects of pre-emptive oxycodone, diclofenac, and gabapentin on postoperative pain after tibia fracture surgery: A randomized clinical trail.J West Afr Coll Surg. 2024 Jul-Sep;14(3):301-306. doi: 10.4103/jwas.jwas_143_23. Epub 2024 May 24. J West Afr Coll Surg. 2024. PMID: 38988418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- V Oldfield, CM Perry. Oxycodone/Ibuprofen Combination Tablet. Drugs. 2005;65:2337–2354. - PubMed
-
- CA Marco, MC Plewa, N Buderer C, Black A. Roberts, Comparison of Oxycodone and Hydrocodone for the Treatment of Acute Pain Associated with Fractures: A Double‐blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Academic emergency medicine. 2005:282–288. - PubMed
-
- ND Moore. In search of an ideal analgesic for common acute pain. Acute Pain. 2009;11:129–137.
-
- SJ Lovell, T Taira, E Rodriguez, A Wackett, J Gulla, AJ Singer. Comparison of valdecoxib and an oxycodone–acetaminophen combination for acute musculoskeletal pain in the emergency department: a randomized controlled trial. Academic emergency medicine. 2004:1278–1282. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources