Salvaging Digital Replantation and Revascularisation: Efficiency of Heparin Solution Subcutaneous Injection
- PMID: 30584577
- PMCID: PMC6280226
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1601738
Salvaging Digital Replantation and Revascularisation: Efficiency of Heparin Solution Subcutaneous Injection
Abstract
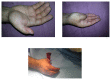
Background: Distal digital replantation and revascularisation remains one of the demanding microsurgical procedures due to the difficulty of vascular anastomosis. Venous congestion is the most commonly encountered problem after replantation due to the difficulty of venous anastomosis in traumatic injuries. Heparin, among other drugs, is commonly used to facilitate venous drainage and prevent thrombosis. However, systemic heparin can be contraindicated in some patients. The senior author has experience of subcutaneous heparin injection for venous congestion in thirteen patients.
Methods: An amount of 1 ml of calcium heparin (25,000 U) was mixed in 2.4 ml of normal saline making a solution that has 1000 U per 0.1 ml. 1000 U (0.1 ml) of the solution was injected directly into the congested replanted digits. This was repeated twice daily until venous congestion improved.
Results: All the congested replanted digits survived without systemic side effects. There were no local side effects of the treatment. The PT and APTT have shown slight increase but they remained within the normal range. Haemoglobin levels have dropped slightly but no patients were at any risk of developing anaemia or needed blood transfusion.
Conclusions: Subcutaneous heparin injections can salvage the replanted digits when venous congestion is a warning flag for replantation failure. It is safe and very efficient in patients where systemic heparin cannot be administered. However, this article shows the results in only thirteen patients which is a small number to show the efficacy, safety, and side effects.
References
-
- Brown JD. Health hazard evaluation report: HETA-96-0171-2692, Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms, Washington, DC. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. 2003 doi: 10.26616/NIOSHHETA9601712692. - DOI
-
- Copuroglu C., Ozcan M., Yilmaz B., Gorgulu Y., Abay E., Yalniz E. Acute stress disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder following traumatic amputation. Acta Orthopædica Belgica. 2010;76(1):90–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources