Copy number loss in SFMBT1 is common among Finnish and Norwegian patients with iNPH
- PMID: 30584596
- PMCID: PMC6283454
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000291
Copy number loss in SFMBT1 is common among Finnish and Norwegian patients with iNPH
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the role of the copy number loss in SFMBT1 in a Caucasian population.
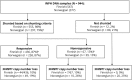
Methods: Five hundred sixty-seven Finnish and 377 Norwegian patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) were genotyped and compared with 508 Finnish elderly, neurologically healthy controls. The copy number loss in intron 2 of SFMBT1 was determined using quantitative PCR.
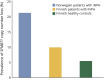
Results: The copy number loss in intron 2 of SFMBT1 was detected in 10% of Finnish (odds ratio [OR] = 1.9, p = 0.0078) and in 21% of Norwegian (OR = 4.7, p < 0.0001) patients with iNPH compared with 5.4% in Finnish controls. No copy number gains in SFMBT1 were detected in patients with iNPH or healthy controls. The carrier status did not provide any prognostic value for the effect of shunt surgery in either population. Moreover, no difference was detected in the prevalence of hypertension or T2DM between SFMBT1 copy number loss carriers and noncarriers.
Conclusions: This is the largest and the first multinational study reporting the increased prevalence of the copy number loss in intron 2 of SFMBT1 among patients with iNPH, providing further evidence of its role in iNPH. The pathogenic role still remains unclear, requiring further study.
Figures
References
-
- Relkin N, Marmarou A, Klinge P, Bergsneider M, Black PM. INPH guidelines, part II: diagnosing idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2005;57:4–16. - PubMed
-
- Mori E, Ishikawa M, Kato T, et al. . Guidelines for management of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: second edition. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2012;52:775–809. - PubMed
-
- Espay AJ, Da Prat GA, Dwivedi AK, et al. . Deconstructing normal pressure hydrocephalus: ventriculomegaly as early sign of neurodegeneration. Ann Neurol 2017:503–513. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
