Effects of Repeated Lipopolysaccharide Treatment on Growth Performance, Immune Organ Index, and Blood Parameters of Sprague-Dawley Rats
- PMID: 30584614
- PMCID: PMC6295989
- DOI: 10.2478/jvetres-2018-0048
Effects of Repeated Lipopolysaccharide Treatment on Growth Performance, Immune Organ Index, and Blood Parameters of Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
Introduction: The study was designed to investigate the effects of repeated lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment on growth performance, lymphoid organ indexes, and blood cells in Sprague-Dawley rats.
Material and methods: Forty healthy weaned Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly equally divided into LPS and control groups. Each rat in the LPS group was injected via the caudal vein with LPS (100 μg/kg b.w.) for 10 days, and the control group was treated with an equal volume of normal saline. On the 1st, 4th, 7th, and 10th days, growth performance, lymphoid organ indexes, and blood cells were evaluated in five necropsied rats.
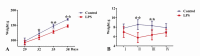
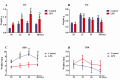
Results: When rats were treated 3-10 times with LPS, their body weight and average daily gains increased more slowly than in the control group (P < 0.05). Repeated LPS treatment significantly increased spleen weight and the ratio of spleen to body weight (P < 0.05). White blood cells, neutrophils, and neutrophil percentage increased (P < 0.05) remarkably, but lymphocyte percentage, haemoglobin, and blood platelet counts decreased significantly (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: LPS treatment obviously suppresses growth and promotes peripheral immune organ proliferation. It is indicated that host protective mechanism can be activated by multiple small doses of LPS and prevents organs from further damage during stress status.
Keywords: blood cells; growth performance; immune organ index; lipopolysaccharide; rat.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests Statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Role of HMGB1-RAGE/TLRs-NF-κB signaling pathway on bone mesenchymal stem cells transplantation therapy for lipopolysaccaride-induced coagulation disorder rats].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Sep;30(9):830-835. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.09.003. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 30309407 Chinese.
-
Effect on the splenocyte function of weaned piglets induced by continuous lipopolysaccharide injections.J Vet Res. 2024 May 9;68(2):295-302. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2024-0024. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38947147 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of radix paeoniae rubra on expression of p38 MAPK/iNOS/HO-1 in rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury.Chin J Traumatol. 2007 Oct;10(5):269-74. Chin J Traumatol. 2007. PMID: 17919363
-
[Protective effect of polyenylphosphatidyl choline on liver in rat with sepsis].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2011 Jul;23(7):401-4. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2011. PMID: 21787467 Chinese.
-
Triptolide ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats.Eur J Med Res. 2013 Dec 17;18(1):58. doi: 10.1186/2047-783X-18-58. Eur J Med Res. 2013. Retraction in: Eur J Med Res. 2015 Mar 26;20:35. doi: 10.1186/s40001-015-0122-8. PMID: 24345260 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
Effects of Probiotics on the Growth Performance, Antioxidant Functions, Immune Responses, and Caecal Microbiota of Broilers Challenged by Lipopolysaccharide.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Feb 21;9:846649. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.846649. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35265699 Free PMC article.
-
A key role of the subdiaphragmatic vagus nerve in the depression-like phenotype and abnormal composition of gut microbiota in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration.Transl Psychiatry. 2020 Jun 9;10(1):186. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-00878-3. Transl Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32518376 Free PMC article.
-
MM165 - A Small Hybrid Molecule Modulates the Kynurenine Pathway and Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Memory Deficits and Inflammation.Neurochem Res. 2024 May;49(5):1200-1211. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04105-z. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38381245
-
Dietary supplementation with mulberry leaf flavonoids and carnosic acid complex enhances the growth performance and antioxidant capacity via regulating the p38 MAPK/Nrf2 pathway.Front Nutr. 2024 Jul 30;11:1428577. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1428577. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39139650 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Sihuang Zhili Granules on the Diarrhea Symptoms, Immunity, and Antioxidant Capacity of Poultry Challenged with Lipopolysaccharide (LPS).Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 30;12(7):1372. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071372. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37507912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campos P.H., Merlot E., Damon M., Noblet J., Le Floc'h N.. High ambient temperature alleviates the inflammatory response and growth depression in pigs challenged with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Vet J. 2014;200:404. –. - PubMed
-
- Cesta M.F.. Normal structure, function, and histology of the spleen. Toxicol Pathol. 2006;34:455. –. - PubMed
-
- Faas M.M., Moes H., van der Schaaf G., de Leij L.F., Heineman M.J.. Total white blood cell counts and LPS-induced TNF alpha production by monocytes of pregnant, pseudopregnant, and cyclic rats. J Reprod Immunol. 2003;59:39. –. - PubMed
-
- Hayley S., Mangano E., Strickland M., Anisman H.. Lipopolysaccharide and a social stressor influence behaviour, corticosterone, and cytokine levels: divergent actions in cyclooxygenase-2 deficient mice and wild type controls. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;197:29. –. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
