Influence of Hydrogen-rich Saline on Hepatocyte Autophagy During Laparoscopic Liver Ischaemia-reperfusion Combined Resection Injury in Miniature Pigs
- PMID: 30584622
- PMCID: PMC6295994
- DOI: 10.2478/jvetres-2018-0056
Influence of Hydrogen-rich Saline on Hepatocyte Autophagy During Laparoscopic Liver Ischaemia-reperfusion Combined Resection Injury in Miniature Pigs
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to investigate the protective effect of hydrogen-rich saline (HRS) against liver ischaemia-reperfusion combined resection injury.
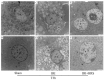
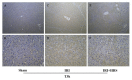
Material and methods: Eighteen miniature pigs were randomly divided into three groups: a sham operated group (sham group, laparoscopic liver ischaemia-reperfusion combined resection injury group (IRI group), and a hydrogen-rich saline intervention group (IRI + HRS group). Samples of hepatic tissue and serum were collected at the time of reperfusion and then 3 h, 1 d, and 3 d post reperfusion. Liver function, oxidative stress, autophagy-related mRNA genes, and protein expression were evaluated. Changes in cell and tissue ultrastructure were examined by transmission electron microscopy.
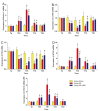
Results: Compared with the sham group, the level of autophagy of hepatocytes increased in the IRI and IRI + HRS groups, corresponding to high oxidative stress and severe liver function injury. Liver function, antioxidant content, autophagy levels, and liver injury were improved after intervention with HRS in the IRI + HRS group compared with the IRI group.
Conclusion: Intervention with hydrogen-rich saline could exert a protective effect against liver ischaemia-reperfusion combined resection injury through the reduction of oxidative stress and hepatocyte autophagy.
Keywords: autophagy; hydrogen-rich saline; ischaemia-reperfusion combined resection; liver; miniature pigs.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests Statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hydrogen-rich saline protects against hepatic injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion and laparoscopic hepatectomy in swine.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2019 Feb;18(1):48-61. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2018.12.001. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2019. PMID: 30573299
-
Hydrogen-rich saline protects against small-scale liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress.Life Sci. 2018 Feb 1;194:7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.12.022. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29253502
-
Comparative study on protective effect of hydrogen rich saline and adipose-derived stem cells on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion and hepatectomy injury in swine.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Dec;120:109453. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109453. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31561069
-
Melatonin and its protective role in attenuating warm or cold hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion injury.Cell Prolif. 2021 Apr;54(4):e13021. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13021. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Cell Prolif. 2021. PMID: 33751704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of autophagy protects against liver injury in liver surgery-induced ischaemia/reperfusion.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Nov;25(21):9905-9917. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16943. Epub 2021 Oct 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34626066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of hydrogen as adjuvant treatment for unstable angina.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Sep;246(18):1981-1989. doi: 10.1177/15353702211009138. Epub 2021 Apr 25. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 33899541 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Endothelial Dysfunction by Regulating Autophagy through mTOR/TFEB Signaling Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jan 30;2020:9121894. doi: 10.1155/2020/9121894. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32071922 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights Into the Role of Autophagy in Liver Surgery in the Setting of Metabolic Syndrome and Related Diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 1;9:670273. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.670273. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34141709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effect of adipose-derived stromal cell-secretome attenuate autophagy induced by liver ischemia-reperfusion and partial hepatectomy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Aug 20;13(1):427. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03109-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35987696 Free PMC article.
-
A Preliminary Study on the Effect of Hydrogen Gas on Alleviating Early CCl4-Induced Chronic Liver Injury in Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 1;10(12):1933. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121933. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baehrecke E.H.. Autophagy: dual roles in life and death? Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:505. –. - PubMed
-
- Codogno P., Meijer A.J.. Autophagy and signaling: their role in cell survival and cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:1509. –. - PubMed
-
- Farre J.C., Subramani S.. Peroxisome turnover by micropexophagy: an autophagy-related process. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:515. –. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
