Targeted exome sequencing of unselected heavy-ion beam-irradiated populations reveals less-biased mutation characteristics in the rice genome
- PMID: 30584677
- PMCID: PMC6850588
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.14213
Targeted exome sequencing of unselected heavy-ion beam-irradiated populations reveals less-biased mutation characteristics in the rice genome
Abstract
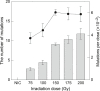
Heavy-ion beams have been widely utilized as a novel and effective mutagen for mutation breeding in diverse plant species, but the induced mutation spectrum is not fully understood at the genome scale. We describe the development of a multiplexed and cost-efficient whole-exome sequencing procedure in rice, and its application to characterize an unselected population of heavy-ion beam-induced mutations. The bioinformatics pipeline identified single-nucleotide mutations as well as small and large (>63 kb) insertions and deletions, and showed good agreement with the results obtained with conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequencing analyses. We applied the procedure to analyze the mutation spectrum induced by heavy-ion beams at the population level. In total, 165 individual M2 lines derived from six irradiation conditions as well as eight pools from non-irradiated 'Nipponbare' controls were sequenced using the newly established target exome sequencing procedure. The characteristics and distribution of carbon-ion beam-induced mutations were analyzed in the absence of bias introduced by visual mutant selections. The average (±SE) number of mutations within the target exon regions was 9.06 ± 0.37 induced by 150 Gy irradiation of dry seeds. The mutation frequency changed in parallel to the irradiation dose when dry seeds were irradiated. The total number of mutations detected by sequencing unselected M2 lines was correlated with the conventional mutation frequency determined by the occurrence of morphological mutants. Therefore, mutation frequency may be a good indicator for sequencing-based determination of the optimal irradiation condition for induction of mutations.
Keywords: heavy-ion beam; mutagenesis; mutation rate; rice (Oryza sativa); whole-exome sequencing.
© 2019 The Authors The Plant Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Time Course Analysis of Genome-Wide Identification of Mutations Induced by and Genes Expressed in Response to Carbon Ion Beam Irradiation in Rice (Oryza sativa L.).Genes (Basel). 2021 Sep 9;12(9):1391. doi: 10.3390/genes12091391. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573373 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequencing of ion-beam-induced mutants facilitates detection of candidate genes responsible for phenotypes of mutants in rice.Mutat Res. 2020 May-Dec;821:111691. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2020.111691. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 32171089
-
Comparison and Characterization of Mutations Induced by Gamma-Ray and Carbon-Ion Irradiation in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Using Whole-Genome Resequencing.G3 (Bethesda). 2019 Nov 5;9(11):3743-3751. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400555. G3 (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 31519747 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to improve the efficiency and quality of mutant breeding using heavy-ion beam irradiation.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2024 Aug;44(5):735-752. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2023.2226339. Epub 2023 Jul 16. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37455421 Review.
-
Mutation breeding of ornamental plants using ion beams.Breed Sci. 2018 Jan;68(1):71-78. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.17086. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Breed Sci. 2018. PMID: 29681749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Consequences of Acute/Chronic Gamma and Carbon Ion Irradiation of Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Mar 25;11:336. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00336. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32273879 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Profile of Mutations Induced by Carbon Ion Beam Irradiation of Dehulled Rice Seeds.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 10;25(10):5195. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105195. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791234 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Efficient and Comprehensive Identification of Ethyl Methanesulfonate-Induced Mutations in Nicotiana tabacum L. by Whole-Genome and Whole-Exome Sequencing.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jun 1;12:671598. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.671598. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34140964 Free PMC article.
-
The Mutational, Epigenetic, and Transcriptional Effects Between Mixed High-Energy Particle Field (CR) and 7Li-Ion Beams (LR) Radiation in Wheat M1 Seedlings.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 11;13:878420. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.878420. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35646033 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of seed and seedling irradiation with gamma rays and carbon ions for mutation induction in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Apr 6;14:1149083. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1149083. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37089645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe, T. , Ryuto, H. and Fukunishi, N. (2012) Ion beam radiation mutagenesis In Plant Mutation Breeding and Biotechnology (Shu Q.Y., Forster B. P. and Nakagawa H., eds). Wallingford: CAB International, pp. 123–134.
-
- Abe, T. , Kazama, Y. and Hirano, T. (2015) Ion beam breeding and gene discovery for function analyses using mutants. Nucl. Phys. News, 25, 30–34.
-
- Andrews, S. (2010) FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Available online at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc.
-
- Bamshad, M.J. , Ng, S.B. , Bigham, A.W. , Tabor, H.K. , Emond, M.J. , Nickerson, D.A. and Shendure, J. (2011) Exome sequencing as a tool for Mendelian disease gene discovery. Nat. Rev. Genet. 12, 745–755. - PubMed
-
- Broad Institute . (2017) Picard tools, version 2.8.2. Available online at: http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard (accessed 27 January 2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

