Higher risk of malignant neoplasms in young adults with end-stage renal disease receiving haemodialysis: A nationwide population-based study
- PMID: 30584693
- PMCID: PMC6849784
- DOI: 10.1111/nep.13555
Higher risk of malignant neoplasms in young adults with end-stage renal disease receiving haemodialysis: A nationwide population-based study
Abstract
Aim: Previous investigations have shown that end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is associated with an increased risk of malignancies. The aim of this study was to explore the association between ESRD in patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis (HD) and the incidence of malignancies according to age.
Methods: We analysed a nationwide cohort retrieved from Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database to study the incidence of malignancies in patients who were and were not receiving HD. One million beneficiaries were randomly selected and followed from 2005 to 2013. Of these 1 000 000 patients, 3055 developed ESRD and commenced maintenance HD during this period. For each HD patient, four age-, gender- and diabetes-matched controls were selected from the database (n = 12 220). We further stratified the patients according to age. The study endpoint was the occurrence of malignancy.
Results: The incidence rates of malignancy were 6.8% and 4.9% in the HD and control groups, respectively. Competing risk regression analysis indicated that age, HD, male gender and diabetes were associated with an increased risk of malignancy. When further stratified according to age, the odds ratios of developing cancer were 5.8, 1.9, 1.9 and 1.5 among the HD patients aged <40 years, 40-49 years, 50-59 years and 60-69 years, respectively.
Conclusion: The patients with ESRD who received HD had a significantly higher cumulative risk of malignancy, especially those with a young age. Therefore, specialized cancer screening protocols for young HD patients might help to prolong their lifespan.
Keywords: end-stage renal disease; haemodialysis; malignancy; young adults.
© 2018 The Authors Nephrology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Asian Pacific Society of Nephrology.
Figures
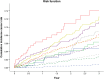
 ) HD 00∼39, (
) HD 00∼39, ( ) HD 40∼49, (
) HD 40∼49, ( ) HD 50∼59, (
) HD 50∼59, ( ) HD 60∼69, (
) HD 60∼69, ( ) HD 70∼79, (
) HD 70∼79, ( ) HD 80up, (
) HD 80up, ( ) non HD 00∼39, (
) non HD 00∼39, ( ) non HD 40∼49, (
) non HD 40∼49, ( ) non HD 50∼59, (
) non HD 50∼59, ( ) non HD 60∼69, (
) non HD 60∼69, ( ) non HD 70∼79, (
) non HD 70∼79, ( ) non HD 80up.
) non HD 80up.Similar articles
-
Dialysis and the risk of early urological cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Taiwan.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 16;104(20):e42521. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042521. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40388720 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing dialysis.Nephrology (Carlton). 2017 May;22(5):397-402. doi: 10.1111/nep.12800. Nephrology (Carlton). 2017. PMID: 27082416
-
Increased risk of incident psoriasis in end-stage renal disease patients on chronic hemodialysis: A nationwide population-based cohort study.J Dermatol. 2018 Sep;45(9):1063-1070. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.14531. Epub 2018 Jul 11. J Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29993144
-
Hemodialysis with end-stage renal disease did not raise the risk of intracranial hemorrhage after a head injury.Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2015 Oct 28;23:82. doi: 10.1186/s13049-015-0168-1. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2015. PMID: 26511383 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Screening in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Dialysis: Who, What, and When.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Oct;76(4):558-566. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.12.018. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 32305205 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Cell Carcinoma Discrimination through Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of Dried Human Urine and Machine Learning Techniques.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 11;25(18):9830. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189830. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337322 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Complex Therapeutic Challenge in the Elderly.Cureus. 2022 Jun 26;14(6):e26346. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26346. eCollection 2022 Jun. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35903561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dialysis and the risk of early urological cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Taiwan.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 16;104(20):e42521. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042521. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40388720 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the risks of renal cell carcinoma or urothelial cancer between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Sep;55(9):2267-2274. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03534-z. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36859625
References
-
- Vajdic CM, McDonald SP, McCredie MRE et al Cancer incidence before and after kidney transplantation. JAMA 2006; 296: 2823–31. - PubMed
-
- Liang J‐A, Sun L‐M, Yeh J‐J, Sung F‐C, Chang S‐N, Kao C‐H. The association between malignancy and end‐stage renal disease in Taiwan. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011; 41: 752–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

