The missing links within troponin
- PMID: 30584890
- PMCID: PMC6377831
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2018.12.026
The missing links within troponin
Abstract
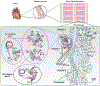
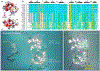
The cardiac contraction-relaxation cycle is controlled by a sophisticated set of machinery. Of particular interest, is the revelation that allosteric networks transmit effects of binding at one site to influence troponin complex dynamics and structural-mediated signaling in often distal, functional sites in the myofilament. Our recent observations provide compelling evidence that allostery can explain the function of large-scale macromolecular events. Here we elaborate on our recent findings of interdomain communication within troponin C, using cutting-edge structural biology approaches, and highlight the importance of unveiling the unknown, distant communication networks within this system to obtain more comprehensive knowledge of how allostery impacts cardiac physiology and disease.
Keywords: Allostery; Dynamics; Structural biology; Thin filament; Troponin.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Farah CS, Reinach FC. The troponin complex and regulation of muscle contraction. Faseb J. 1995;9:755–67. - PubMed
-
- Bagshaw CR. Muscle contraction. 2nd ed. London ; New York: Chapman & Hall; 1993.
-
- Tobacman LS. Thin filament-mediated regulation of cardiac contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1996;58:447–81. - PubMed
-
- Solaro RJ. Integration of myofilament response to Ca2+ with cardiac pump regulation and pump dynamics. The American journal of physiology. 1999;277:S155–63. - PubMed
-
- Bers DM. Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 2002;415:198–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

