Haptoglobin 2 Allele is Associated With Histologic Response to Vitamin E in Subjects With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- PMID: 30586008
- PMCID: PMC6588507
- DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001142
Haptoglobin 2 Allele is Associated With Histologic Response to Vitamin E in Subjects With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Abstract
Background: Haptoglobin (Hp) genotype has been linked to oxidative stress and cardiovascular outcomes in response to vitamin E (VitE) among patients with diabetes mellitus. Its effect on histologic response to VitE in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is unknown.
Goals: Our objective was to determine if Hp genotype associates with response to VitE in patients with NASH.
Study: A post hoc analysis of 228 patients receiving VitE or placebo in 2 clinical trials was performed. Regression analysis was used to assess the effect of VitE versus placebo, by Hp genotype (1-1, 2-1, or 2-2), on histologic features and laboratory markers of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, comparing baseline to end of treatment values. An interaction term was included in the regression models to assess differential treatment effect across Hp genotype.
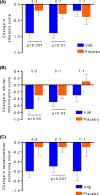
Results: Hp 2-2 patients treated with VitE versus placebo showed significant histologic improvement (51% vs. 20%; OR=4.2; P=0.006), resolution of steatohepatitis (44% vs. 12%; OR=6.2; P=0.009), decrease in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease Activity Score (NAS) (-2.2 vs. -0.6; P=0.001), and decrease in liver enzymes alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. Hp 2-1 patients on VitE versus placebo showed improved resolution of steatohepatitis, NAS and liver enzymes. Hp 1-1 patients showed no significant improvement in histology or liver enzymes. VitE had no effect on fibrosis stage in any group. Regression analysis showed incremental benefit of having Hp 2-2 or 2-1 versus 1-1 for all liver enzyme.
Conclusions: Hp 2 allele is associated with greater histologic and biological improvement in NASH with VitE treatment compared with the Hp 1 allele.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report. Dr. Sanyal is President of Sanyal Biotechnology and has stock options in Genfit, Akarna, Tiziana, Indalo, Durect and Galmed. He has served as a consultant to Astra Zeneca, Nitto Denko, Enyo, Ardelyx, Conatus, Nimbus, Amarin, Salix, Tobira, Takeda, Jannsen, Gilead, Terns, Birdrock, Merck, Valeant, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Lilly, Hemoshear, Zafgen, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Exhalenz and Genfit. He has been an unpaid consultant to Intercept, Echosens, Immuron, Galectin, Fractyl, Syntlogic, Affimune, Chemomab, Zydus, Nordic Bioscience, Albireo, Prosciento, Surrozen and Bristol Myers Squibb. His institution has received grant support from Gilead, Salix, Tobira, Bristol Myers, Shire, Intercept, Merck, Astra Zeneca, Malinckrodt, Cumberland and Novartis. He receives royalties from Elsevier and UptoDate.
Figures

References
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology 2012;55:2005–23. - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Deeg MA, Crabb DW. Systemic levels of lipid peroxidation and its metabolic and dietary correlates in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. The American journal of gastroenterology 2004;99:1497–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R03 DK081450/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000006/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK105961/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000058/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000436/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007150/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR001107/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002548/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK061730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002319/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000077/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000423/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000100/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081410/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003098/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

