The genus Borrelia reloaded
- PMID: 30586413
- PMCID: PMC6306154
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208432
The genus Borrelia reloaded
Abstract
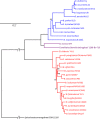
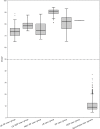
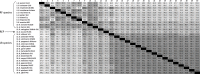
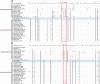
The genus Borrelia, originally described by Swellengrebel in 1907, contains tick- or louse-transmitted spirochetes belonging to the relapsing fever (RF) group of spirochetes, the Lyme borreliosis (LB) group of spirochetes and spirochetes that form intermittent clades. In 2014 it was proposed that the genus Borrelia should be separated into two genera; Borrelia Swellengrebel 1907 emend. Adeolu and Gupta 2014 containing RF spirochetes and Borreliella Adeolu and Gupta 2014 containing LB group of spirochetes. In this study we conducted an analysis based on a method that is suitable for bacterial genus demarcation, the percentage of conserved proteins (POCP). We included RF group species, LB group species and two species belonging to intermittent clades, Borrelia turcica Güner et al. 2004 and Candidatus Borrelia tachyglossi Loh et al. 2017. These analyses convincingly showed that all groups of spirochetes belong into one genus and we propose to emend, and re-unite all groups in, the genus Borrelia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Comment in
-
Distinction between Borrelia and Borreliella is more robustly supported by molecular and phenotypic characteristics than all other neighbouring prokaryotic genera: Response to Margos' et al. "The genus Borrelia reloaded" (PLoS ONE 13(12): e0208432).PLoS One. 2019 Aug 27;14(8):e0221397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221397. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31454394 Free PMC article.
-
Comment on: Gupta, 2019, distinction between Borrelia and Borreliella is more robustly supported by molecular and phenotypic characteristics than all other neighbouring prokaryotic genera: Response to Margos' et al. "The genus Borrelia reloaded" (PLoS One 13(12): e0208432). PLoS One 14(8):e0221397.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020 Mar;11(2):101320. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2019.101320. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020. PMID: 31722850 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

