Tofacitinib Treatment and Molecular Analysis of Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
- PMID: 30586518
- PMCID: PMC6351852
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1805958
Tofacitinib Treatment and Molecular Analysis of Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
Abstract
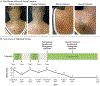
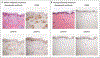
There is evidence that Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling plays a role in the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis. We treated a patient with cutaneous sarcoidosis with the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib; the patient had not previously had a response to medications and had not received systemic glucocorticoids. This treatment resulted in clinical and histologic remission of her skin disease. Sequencing of RNA and immunohistochemical examination of skin-lesion samples obtained from the patient before and during therapy and immunohistochemical testing of lesion samples obtained from other patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis support a role for JAK-STAT signaling in cutaneous sarcoidosis. (Funded by the Ranjini and Ajay Poddar Resource Fund for Dermatologic Diseases Research and others.).
Figures
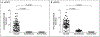
Similar articles
-
Tofacitinib for cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoidosis: A case series.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021 Feb;84(2):581-583. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.10.016. Epub 2020 Oct 16. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33075414 No abstract available.
-
Janus kinase inhibition induces disease remission in cutaneous sarcoidosis and granuloma annulare.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Mar;82(3):612-621. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.05.098. Epub 2019 Jun 8. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31185230 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of JAK/STAT signaling in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Oct;76:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23827161 Review.
-
Tofacitinib, an Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitor: Perspectives in Dermatology.Curr Med Chem. 2017 May 31;24(11):1158-1167. doi: 10.2174/1874467210666170113104503. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28088907 Review.
-
Osteoimmunology in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis: potential effects of tofacitinib on bone involvement.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Mar;39(3):727-736. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-04930-x. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31970549 Review.
Cited by
-
The biological basis for current treatment strategies for granulomatous disease in common variable immunodeficiency.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 Dec 1;24(6):479-487. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000001032. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39431514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of the pentose phosphate pathway in macrophages is crucial for granuloma formation in sarcoidosis.J Clin Invest. 2023 Dec 1;133(23):e171088. doi: 10.1172/JCI171088. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 38038136 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Sarcoidosis in US Rheumatology Practices: Data From the American College of Rheumatology's Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE) Registry.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022 Mar;74(3):371-376. doi: 10.1002/acr.24496. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022. PMID: 33105057 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Sarcoidosis-The great mimicker.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 2;9:990714. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.990714. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35983097 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Fats and the Furious: Unraveling the Role of Macrophage Lipid Metabolism in Sarcoidosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 May 1;209(9):1064-1066. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202402-0287ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38690977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Noe MH, Rosenbach M. Cutaneous sarcoidosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2017; 23: 482–6. - PubMed
-
- Spagnolo P, Rossi G, Trisolini R, Sverzellati N, Baughman RP, Wells AU. Pulmonary sarcoidosis. Lancet Respir Med 2018; 6: 389–402. - PubMed
-
- Zissel G, Müller-Quernheim J. Cellular players in the immunopathogenesis of sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med 2015; 36: 549–60. - PubMed
-
- Broos CE, Hendriks RW, Kool M. T-cell immunology in sarcoidosis: disruption of a delicate balance between helper and regulatory T-cells. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2016; 22: 476–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
