Genome-Wide Association Transethnic Meta-Analyses Identifies Novel Associations Regulating Coagulation Factor VIII and von Willebrand Factor Plasma Levels
- PMID: 30586737
- PMCID: PMC6438386
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034532
Genome-Wide Association Transethnic Meta-Analyses Identifies Novel Associations Regulating Coagulation Factor VIII and von Willebrand Factor Plasma Levels
Abstract
Background: Factor VIII (FVIII) and its carrier protein von Willebrand factor (VWF) are associated with risk of arterial and venous thrombosis and with hemorrhagic disorders. We aimed to identify and functionally test novel genetic associations regulating plasma FVIII and VWF.
Methods: We meta-analyzed genome-wide association results from 46 354 individuals of European, African, East Asian, and Hispanic ancestry. All studies performed linear regression analysis using an additive genetic model and associated ≈35 million imputed variants with natural log-transformed phenotype levels. In vitro gene silencing in cultured endothelial cells was performed for candidate genes to provide additional evidence on association and function. Two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses were applied to test the causal role of FVIII and VWF plasma levels on the risk of arterial and venous thrombotic events.
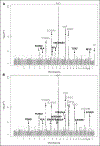
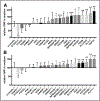
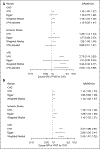
Results: We identified 13 novel genome-wide significant ( P≤2.5×10-8) associations, 7 with FVIII levels ( FCHO2/TMEM171/TNPO1, HLA, SOX17/RP1, LINC00583/NFIB, RAB5C-KAT2A, RPL3/TAB1/SYNGR1, and ARSA) and 11 with VWF levels ( PDHB/PXK/KCTD6, SLC39A8, FCHO2/TMEM171/TNPO1, HLA, GIMAP7/GIMAP4, OR13C5/NIPSNAP, DAB2IP, C2CD4B, RAB5C-KAT2A, TAB1/SYNGR1, and ARSA), beyond 10 previously reported associations with these phenotypes. Functional validation provided further evidence of association for all loci on VWF except ARSA and DAB2IP. Mendelian randomization suggested causal effects of plasma FVIII activity levels on venous thrombosis and coronary artery disease risk and plasma VWF levels on ischemic stroke risk.
Conclusions: The meta-analysis identified 13 novel genetic loci regulating FVIII and VWF plasma levels, 10 of which we validated functionally. We provide some evidence for a causal role of these proteins in thrombotic events.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; factor VIII; genetics; genome-wide association studies; risk factors; von Willebrand factor.
Figures
References
-
- Folsom AR. Hemostatic risk factors for atherothrombotic disease: an epidemiologic view. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86:366–373. - PubMed
-
- Koster T, Blann AD, Briët E, Vandenbroucke JP, Rosendaal FR. Role of clotting factor VIII in effect of von Willebrand factor on occurrence of deep-vein thrombosis. Lancet. 1995;345:152–155. - PubMed
-
- Smith A, Patterson C, Yarnell J, Rumley A, Ben-Shlomo Y, Lowe G. Which hemostatic markers add to the predictive value of conventional risk factors for coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke? The Caerphilly Study. Circulation. 2005;112:3080–3087. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.557132 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_UU_00007/10/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UH3 NS100605/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG007380/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135793/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 AG999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134894/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

