Human Periprostatic Adipose Tissue: Secretome from Patients With Prostate Cancer or Benign Prostate Hyperplasia
- PMID: 30587498
- PMCID: PMC6348399
- DOI: 10.21873/cgp.20110
Human Periprostatic Adipose Tissue: Secretome from Patients With Prostate Cancer or Benign Prostate Hyperplasia
Abstract
Background/aim: Periprostatic adipose tissue (PPAT) directs tumour behaviour. Microenvironment secretome provides information related to its biology. This study was performed to identify secreted proteins by PPAT, from both prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) patients.
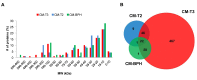
Patients and methods: Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis was performed in PPAT-conditioned media (CM) from patients with prostate cancer (CMs-T) (stage T3: CM-T3, stage T2: CM-T2) or benign disease (CM-BPH).
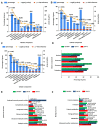
Results: The highest number and diversity of proteins was identified in CM-T3. Locomotion was the biological process mainly associated to CMs-T and reproduction to CM-T3. Immune responses were enriched in CMs-T. Extracellular matrix and structural proteins were associated to CMs-T. CM-T3 was enriched in proteins with catalytic activity and CM-T2 in proteins with defense/immunity activity. Metabolism and energy pathways were enriched in CM-T3 and those with immune system functions in CMs-T. Transport proteins were enriched in CM-T2 and CM-BPH.
Conclusion: Proteins and pathways reported in this study could be useful to distinguish stages of disease and may become targets for novel therapies.
Keywords: Periprostatic adipose tissue; benign prostate hyperplasia; fat tissue; microenvironment; prostate cancer; proteomic; secretome.
Copyright© 2019, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors have no potential conflict of interest in the present work.
Figures



References
-
- Hong H, Koch MO, Foster RS, Bihrle R, Gardner TA, Fyffe J, Ulbright TM, Eble JN, Cheng L. Anatomic distribution of periprostatic adipose tissue: a mapping study of 100 radical prostatectomy specimens. Cancer. 2003;97(7):1639–1643. - PubMed
-
- Mistry T, Digby JE, Desai KM, Randeva HS. Obesity and prostate cancer: a role for adipokines. Eur Urol. 2007;52(1):46–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
