Serological and histological evaluation of species-specific immunocontraceptive vaccine antigens based on zona pellucida 3 in the small Indian mongoose (Herpestes auropunctatus)
- PMID: 30587673
- PMCID: PMC6395204
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.17-0605
Serological and histological evaluation of species-specific immunocontraceptive vaccine antigens based on zona pellucida 3 in the small Indian mongoose (Herpestes auropunctatus)
Abstract
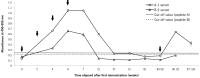
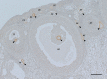
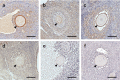
The small Indian mongoose (Herpestes auropunctatus) was introduced to Japanese islands and has impacted on the island's biodiversity. Population control has been attempted through capturing but its efficiency has rapidly declined. Therefore, new additional control methods are required. Our focus has been on the immunocontraceptive vaccines, which act in an especially species-specific manner. The amino-acid sequence of the mongoose ovum zona pellucida protein 3 (ZP3) was decoded and two types of synthetic peptides (A and B) were produced. In this study, these peptides were administered to mongooses (each n=3) and the sera were collected to verify immunogenicity using ELISA and IHC. Treated mongoose sera showed an increasing of antibody titer according to immunizations and the antigen-antibody reactions against the endogenous mongoose ZP. In addition, IHC revealed that immune sera absorbed with each peptide showed a marked reduction in reactivity, which indicated the specificity of induced antibodies. These reactions were marked in peptide A treated mongoose sera, and the antibody titer of one of them lasted for at least 21 weeks. These results indicated that peptide A was a potential antigen, inducing autoantibody generation. Moreover, immunized rabbit antibodies recognized mongoose ZP species-specifically. However, the induction of robust immune memory was not observed. Also, the actual sterility effects of peptides remain unknown, it should be verified as a next step. In any case, this study verified synthetic peptides we developed are useful as the antigen candidates for immunocontraception of mongooses.
Keywords: fertility control; immunocontraception; invasive alien species; mongoose; zona pellucida.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Strategies for designing an immunocontraceptive vaccine based on zona pellucida synthetic peptides and recombinant antigen.J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1996;50:127-34. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8984175
-
Contraceptive potential of porcine and feline zona pellucida A, B and C subunits in domestic cats.Reproduction. 2009 Jun;137(6):913-22. doi: 10.1530/REP-08-0471. Epub 2009 Mar 11. Reproduction. 2009. PMID: 19279201
-
Evaluation of zona pellucida antigens as potential candidates for immunocontraception.J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1996;50:175-82. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8984181
-
Immunocontraception: consideration of the zona pellucida as a target antigen.Obstet Gynecol Annu. 1981;10:1-26. Obstet Gynecol Annu. 1981. PMID: 6168990 Review.
-
Targeting the zona pellucida for immunocontraception: a minireview.Hum Reprod. 1995 Dec;10 Suppl 2:132-9. doi: 10.1093/humrep/10.suppl_2.132. Hum Reprod. 1995. PMID: 8745311 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Contraceptive Vaccine Development: A Comprehensive Review.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;13(7):692. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13070692. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40733669 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe S.1995. Age determination of mongoose on Amami-oshima Island based on eye lens weight. Chirimosu 6: 34–43(in Japanese).
-
- Akatsuka K., Yoshida-Komiya H., Tulsiani D. R. P., Orgebin-Crist M. C., Hiroi M., Araki Y.1998. Rat zona pellucida glycoproteins: molecular cloning and characterization of the three major components. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 51: 454–467. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199812)51:4<454::AID-MRD13>3.0.CO;2-G - DOI - PubMed

