Identification and Functional Characterization of a Cold-Related Protein, BcHHP5, in Pak-Choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis)
- PMID: 30587842
- PMCID: PMC6337265
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20010093
Identification and Functional Characterization of a Cold-Related Protein, BcHHP5, in Pak-Choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis)
Abstract
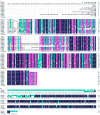
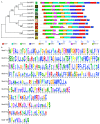
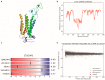
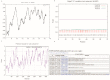
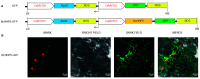
In plants, heptahelical proteins (HHPs) have been shown to respond to a variety of abiotic stresses, including cold stress. Up to the present, the regulation mechanism of HHP5 under low temperature stress remains unclear. In this study, BcHHP5 was isolated from Pak-choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis cv. Suzhouqing). Sequence analysis and phylogenetic analysis indicated that BcHHP5 in Pak-choi is similar to AtHHP5 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Structure analysis showed that the structure of the BcHHP5 protein is relatively stable and highly conservative. Subcellular localization indicated that BcHHP5 was localized on the cell membrane and nuclear membrane. Furthermore, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis showed that BcHHP5 was induced to express by cold and other abiotic stresses. In Pak-choi, BcHHP5-silenced assay, inhibiting the action of endogenous BcHHP5, indicated that BcHHP5-silenced might have a negative effect on cold tolerance, which was further confirmed. All of these results indicate that BcHHP5 might play a role in abiotic response. This work can serve as a reference for the functional analysis of other cold-related proteins from Pak-choi in the future.
Keywords: Pak-Choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis); cold-related; heptahelical protein 5; virus-induced gene silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
BcMAF2 activates BcTEM1 and represses flowering in Pak-choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis).Plant Mol Biol. 2019 May;100(1-2):19-32. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00867-1. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Plant Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31001712
-
Characterization and co-expression analysis of WRKY orthologs involved in responses to multiple abiotic stresses in Pak-choi (Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis).BMC Plant Biol. 2013 Nov 25;13:188. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-13-188. BMC Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 24267479 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and Functional Analysis of BcMYB101 Gene Involved in Leaf Development in Pak Choi (Brassica rapa ssp. Chinensis).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;21(8):2750. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082750. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326634 Free PMC article.
-
A novel cold-inducible gene from Pak-choi (Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis), BcWRKY46, enhances the cold, salt and dehydration stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Apr;39(4):4553-64. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-1245-9. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 21938429
-
Isolation and functional characterization of a floral repressor, BcFLC2, from Pak-choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis).Planta. 2018 Aug;248(2):423-435. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2891-0. Epub 2018 May 14. Planta. 2018. PMID: 29761290
Cited by
-
MsSPL12 is a positive regulator in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) salt tolerance.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Mar 18;43(4):101. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03175-1. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38498195
-
Upregulation of CD271 transcriptome in breast cancer promotes cell survival via NFκB pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jan;49(1):487-495. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06900-1. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34755264
-
Genome-wide analysis of the SPL family in Zanthoxylum armatum and ZaSPL21 promotes flowering and improves salt tolerance in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana.Plant Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 20;115(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s11103-024-01530-0. Plant Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39832014
-
Genome-wide identification, stress- and hormone-responsive expression characteristics, and regulatory pattern analysis of Scutellaria baicalensis SbSPLs.Plant Mol Biol. 2024 Feb 16;114(2):20. doi: 10.1007/s11103-023-01410-z. Plant Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38363403 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Pathogenesis of Cardiotoxicity: Diagnostic & Prognostic Approach.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep;65(9):1403-1413. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00697-z. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36847962 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

