MMI-0100 ameliorates lung inflammation in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome by reducing endothelial expression of ICAM-1
- PMID: 30587921
- PMCID: PMC6296205
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S188095
MMI-0100 ameliorates lung inflammation in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome by reducing endothelial expression of ICAM-1
Abstract
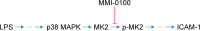
Purpose: ICAM-1 plays a critical role in the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). MK2 regulates the expression of ICAM-1 in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. To explore whether the inhibition of MK2 activation has the same effect in experimental animals, MMI-0100, a peptide-mediated inhibitor of MK2, was used to verify whether MMI-0100 can ameliorate lung inflammation in a mouse model of ARDS by reducing endothelial expression of ICAM-1.
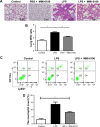
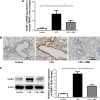
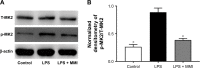
Methods: In this study, C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into three groups: a control group, an lipopolysaccharides (LPS) group, and an LPS plus MMI-0100 group. Mice were killed 24 hours after the administration of LPS and MMI-0100. The mouse lung tissue histopathology, wet/dry weight ratio (W/D), and the neutrophil count were used to measure the severity of lung inflammation in mice. The pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs) of the mice were isolated. The mRNA expression of ICAM-1 in mouse PMVECs was determined using RT-PCR, and the protein expression of MK2 and ICAM-1 in mouse PMVECs was analyzed using Western blotting and immunohistochemistry.
Results: We found that the level of phosphorylated MK2 in the LPS plus MMI-0100 group was reduced. Compared with the LPS group, the LPS plus MMI-0100 group of mice showed less severe inflammation, including a lower W/D and neutrophil count. The mRNA and protein expression of ICAM-1 in the LPS group was significantly higher than in the control group in mouse PMVECs, and the ICAM-1 level was reduced after the administration of MMI-0100.
Conclusion: These data indicate that MMI-0100 ameliorates lung inflammation in a mouse model of ARDS by reducing endothelial expression of ICAM-1.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; inflammation; pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(16):1685–1693. - PubMed
-
- Montefort S, Roche WR, Howarth PH, et al. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and endothelial leucocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) expression in the bronchial mucosa of normal and asthmatic subjects. Eur Respir J. 1992;5(7):815–823. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

