3- n-butylphthalide exerts neuroprotective effects by enhancing anti-oxidation and attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction in an in vitro model of ischemic stroke
- PMID: 30587922
- PMCID: PMC6298396
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S189472
3- n-butylphthalide exerts neuroprotective effects by enhancing anti-oxidation and attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction in an in vitro model of ischemic stroke
Abstract
Purpose: This study examined whether the neuroprotective drug, 3-n-butylphthalide (NBP), which is used to treat ischemic stroke, prevents mitochondrial dysfunction.
Materials and methods: PC12 neuronal cells were pretreated for 24 hours with NBP (10 μmol/L), then exposed to oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) for 8 hours as an in vitro model of ischemic stroke. Indices of anti-oxidative response, mitochondrial function and mitochondrial dynamics were evaluated.
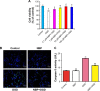
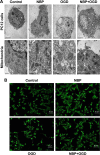
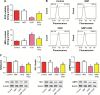
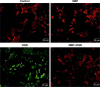
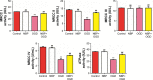
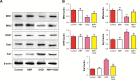
Results: OGD suppressed cell viability, induced apoptosis and increased caspase-3 activity. NBP significantly reversed these effects. NBP prevented oxidative damage by increasing the activity of superoxide dismutase and lowering levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and reactive oxygen species (ROS). At the same time, it increased expression of Nrf2, HO-1 and AMPK. NBP attenuated mitochondrial dysfunction by enhancing mitochondrial membrane potential and increasing the activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes I-IV and ATPase. NBP altered the balance of proteins regulating mitochondrial fusion and division.
Conclusion: NBP exerts neuroprotective actions by enhancing anti-oxidation and attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction. Our findings provide insight into how NBP may exert neuroprotective effects in ischemic stroke and raise the possibility that it may function similarly against other neurodegenerative diseases involving mitochondrial dysfunction.
Keywords: ischemic stroke; mitochondrial dynamics; mitochondrial dysfunction; neuroprotective.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Khoshnam SE, Sarkaki A, Rashno M, Farbood Y. Memory deficits and hippocampal inflammation in cerebral hypoperfusion and reperfusion in male rats: neuroprotective role of vanillic acid. Life Sci. 2018;211:126–132. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

