Multimetal organic frameworks as drug carriers: aceclofenac as a drug candidate
- PMID: 30587925
- PMCID: PMC6305134
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S182983
Multimetal organic frameworks as drug carriers: aceclofenac as a drug candidate
Abstract
Background: Multimetal organic frameworks (M-MOFs) were synthesized by including a second metal ion with the main base metal in the synthesis process to enhance their applications for drug delivery. Aceclofenac (ACF), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory analgesic drug of low aqueous solubility, was selected as a candidate for the drug delivery system.
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the loading capacity (LC) and entrapment efficiency (EE) percentages of multi-Material of Institute Lavoisier (MIL)-100(Fe) (M-MIL-100(Fe)) for ACF.
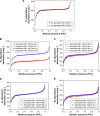
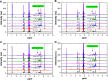
Materials and methods: Hydrothermal synthesis procedure was used to prepare multi-MIL-100(Fe) samples (Zn I-MIL-100(Fe), Zn II-MIL-100(Fe), Ca I-MIL-100(Fe), Ca II-MIL-100-(Fe), Mg I-MIL-100(Fe), Mg II-MIL-100(Fe), Mn I-MIL-100(Fe), and Mn II-MIL-100(Fe)). The characterization of M-MIL-100(Fe) samples was evaluated by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectra, scanning electron microscope (SEM), TGA, and N2 adsorption isotherms. The LC of M-MIL-100(Fe) and EE of ACF were determined. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and zeta-potential analyses were employed to confirm qualitatively the drug loading within M-MIL-100(Fe).
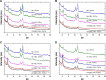
Results: The ACF LC of MIL-100(Fe) was 27%, whereas the LC of M-MIL-100(Fe) was significantly increased and ranged from 37% in Ca I-MIL-100(Fe) to about 57% and 59% in Mn II-MIL-100(Fe) and Zn II-MIL-100(Fe), respectively. The ACF@M-MOFs release profiles showed slow release rates in phosphate buffer solutions at pH 6.8 and 7.4 as compared to the ACF@MIL-100(Fe).
Conclusion: Therefore, M-MOFs showed a significant potential as a carrier for drug delivery systems.
Keywords: MIL-100; Mixed metal-MOF; aceclofenac; drug delivery; drug loading.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Valizadeh B, Nguyen TN, Stylianou KC. Shape engineering of metal–organic frameworks. Polyhedron. 2018;145:1–15.
-
- Furukawa H, Cordova KE, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi OM. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science. 2013;341(6149):1230444. - PubMed
-
- Pettinari C, Marchetti F, Mosca N, Tosi G, Drozdov A. Application of metal − organic frameworks. Polym Int. 2017;66(6):731–744.
-
- Sun CY, Qin C, Wang XL, Su ZM. Metal-organic frameworks as potential drug delivery systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2013;10(1):89–101. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

