Liposome delivery systems for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 30587974
- PMCID: PMC6296687
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S183117
Liposome delivery systems for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) will affect around 115 million people worldwide by the year 2050. It is associated with the accumulation of misfolded and aggregated proteins (β-amyloid and tau) in the senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles found in the brain. Currently available drugs for AD only temporarily alleviate symptoms and do not slow the inevitable progression of this disease. New drugs are required that act on key pathologies in order to arrest or reverse cognitive decline. However, there has been a spectacular failure rate in clinical trials of conventional small molecule drugs or biological agents. Targeted nanoliposomes represent a viable and promising drug delivery system for AD that have not yet reached clinical trials. They are biocompatible, highly flexible, and have the potential to carry many different types of therapeutic molecules across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and into brain cells. They can be tailored to extend blood circulation time and can be directed against individual or multiple pathological targets. Modifications so far have included the use of brain-penetrating peptides, together with Aβ-targeting ligands, such as phosphatidic acid, curcumin, and a retro-inverted peptide that inhibits Aβ aggregation. Combining several modifications together into multifunctional liposomes is currently a research area of great interest. This review focuses on recent liposomal approaches to AD therapy, including mechanisms involved in facilitating their passage across the BBB, and the evaluation of new therapeutic agents for blocking Aβ and/or tau aggregation.
Keywords: amyloid; blood-brain barrier; cell-penetrating peptides; neurofibrillary tangles; senile plaques; tau.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Lancaster University has a granted patent on intellectual property related to this area of research based on the inventions of DA and MT. The other authors (CR and NF) report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
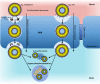
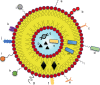
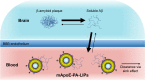
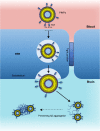
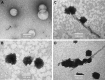
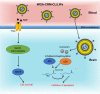
References
-
- World Health Organization . Neurological Disorders: Public Health Challenges. Geneva: WHO; 2006.
-
- Krstic D, Knuesel I. Deciphering the mechanism underlying late-onset Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013;9(1):25–34. - PubMed
-
- Karran E, de Strooper B. The amyloid cascade hypothesis: are we poised for success or failure? J Neurochem. 2016;139(Suppl 2):237–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

