Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Albizia lebbeck stem bark, and evaluation of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities on human breast cancer cell lines
- PMID: 30587987
- PMCID: PMC6304255
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S186888
Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Albizia lebbeck stem bark, and evaluation of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities on human breast cancer cell lines
Abstract
Background: Biocompatibility and stability of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) synthesized using plants is an interesting research area of study in nanotechnology, due to its wide applications in biomedical, industrial, cell imaging, and biosensor fields. The present study reports the novel green synthesis of stable ZnO NPs using various concentrations of zinc nitrate (0.01M, 0.05M, 0.1M) and Albizia lebbeck stem bark extracts as an efficient chelating agent. Antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, and antiproliferative activities of the synthesized NPs on human breast cancer cell lines were evaluated using different assays.
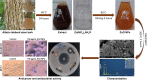
Methods: Characterization of the synthesized ZnO NPs were carried out using various spectroscopic and microscopic techniques. Antimicrobial activity evaluation using disc diffusion method, antioxidant activity using hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) free radical scavenging assay and cytotoxic activity on MDA-MB 231 and MCF-7 using tryphan blue dye exclusion and MTT assay.
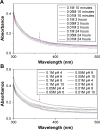
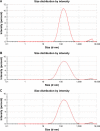
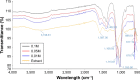
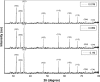
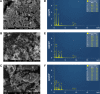
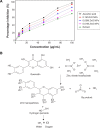
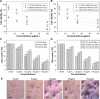
Results: The UV-vis spectroscopy result revealed an absorption peak in the range of 370 nm. The involvements of A. lebbeck bioactive compounds in the stabilization of the ZnO NPs were confirmed by X-ray diffraction and Fourier transform infrared analysis. Zeta sizer studies showed an average size of 66.25 nm with a polydisparity index of 0.262. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analyses results revealed irregular spherical morphology and the presence of primarily Zn, C, O, Na, P, and K, respectively. The biosynthesized ZnO NPs revealed strong antimicrobial potentials against various gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial pathogens. Antioxidant activities carried out using H2O2 free radical scavenging assay revealed higher IC50 values of 48.5, 48.7, and 60.2 µg/mL for 0.1M, 0.05M, and 0.01M ZnO NPs, respectively. Moreover, the biosynthesized ZnO NPs showed significant cytotoxic effects on MDA-MB 231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines (P< 0.001, n≥3) in a concentration-dependent manner.
Conclusion: Overall, various concentrations of ZnO NPs were synthesized through a stable, simple, and eco-friendly green route via the use of A. lebbeck stem bark extract. The biosynthesized ZnO NPs showed strong antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activity against strongly and weakly metastatic breast cancer cell lines.
Keywords: antimicrobial; antioxidant; biocompatibility; biosynthesis; cytotoxic.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Albrecht MA, Evans CW, Raston CL. Green chemistry and the health implications of nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2006;8(5):417–432.
-
- Xu D, Liu M, Zou H, et al. A new strategy for fabrication of water dispersible and biodegradable fluorescent organic nanoparticles with AIE and ESIPT characteristics and their utilization for bioimaging. Talanta. 2017;174:803–808. - PubMed
-
- Hassan HF, Mansour AM, Abo-Youssef AM, Elsadek BE, Messiha BA. Zinc oxide nanoparticles as a novel anticancer approach; in vitro and in vivo evidence. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;44(2):235–243. - PubMed
-
- Nirmala M, Anukaliani A. Synthesis and characterization of undoped and TM (Co, Mn) doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater Lett. 2011;65(17–18):2645–2648.
-
- Thapa A, Soares AC, Soares JC, et al. Carbon nanotube matrix for highly sensitive biosensors to detect pancreatic cancer biomarker CA19-9. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(31):25878–25886. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

