Calcium and vitamin D supplementation with 3-year denosumab treatment is beneficial to enhance bone mineral density in postmenopausal patients with osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 30588001
- PMCID: PMC6302805
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S182858
Calcium and vitamin D supplementation with 3-year denosumab treatment is beneficial to enhance bone mineral density in postmenopausal patients with osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: This 3-year retrospective study compared the outcomes of bisphosphonate-pretreated denosumab therapy with or without vitamin D and calcium supplementation in postmenopausal osteoporosis (OP) patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
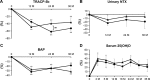
Materials and methods: Fifty-eight patients under long-term denosumab treatment were divided into groups without (denosumab group; 31 cases) or with (combination group; 27 cases) vitamin D and calcium supplementation. The bone markers of BAP, TRACP-5b, and urinary NTX were measured at baseline and every year for 3 years. We also evaluated bone mineral density (BMD) of the lumbar 1-4 vertebrae (L-BMD) and bilateral total hips (H-BMD) at the same time points.
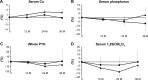
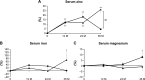
Results: There were no significant differences in the percent changes of serum albumin-corrected calcium between the groups. The percent change in TRACP-5b was significantly higher in the combination group at 2 years. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status was persistently high during therapy in both groups, with significant percent increases over baseline at 2 and 6 months in both groups and at 24 months in the combination group. The percent increase from baseline of serum zinc was significantly higher at 3 years in the combination group over the denosumab group. L-BMD and H-BMD were significantly increased at every time point for 3 years vs pretreatment levels in both groups and were significantly higher in the combination group at all time points.
Conclusion: Compared with denosumab monotherapy, the combination group displayed significantly increased serum zinc, L-BMD, and H-BMD at 3 years in OP patients with RA. Thus, calcium and vitamin D supplementation may be beneficial to enhance BMD gains, but not necessarily 25-hydroxyvitamin D status, in patients with OP and RA under denosumab.
Keywords: 25(OH)D; bone mineral density; bone-related minerals; denosumab; osteoporosis; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Denosumab significantly improves bone mineral density with or without bisphosphonate pre-treatment in osteoporosis with rheumatoid arthritis : Denosumab improves bone mineral density in osteoporosis with rheumatoid arthritis.Arch Osteoporos. 2017 Sep 21;12(1):80. doi: 10.1007/s11657-017-0371-y. Arch Osteoporos. 2017. PMID: 28936606
-
Vitamin D and Calcium Are Required during Denosumab Treatment in Osteoporosis with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Nutrients. 2017 Apr 26;9(5):428. doi: 10.3390/nu9050428. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28445420 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and Calcium Addition during Denosumab Therapy over a Period of Four Years Significantly Improves Lumbar Bone Mineral Density in Japanese Osteoporosis Patients.Nutrients. 2018 Feb 27;10(3):272. doi: 10.3390/nu10030272. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29495518 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and calcium are required at the time of denosumab administration during osteoporosis treatment.Bone Res. 2017 Oct 10;5:17021. doi: 10.1038/boneres.2017.21. eCollection 2017. Bone Res. 2017. PMID: 29021920 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of denosumab on bone metabolism and bone mineral density in kidney transplant patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Osteoporos. 2019 Mar 9;14(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s11657-019-0587-0. Arch Osteoporos. 2019. PMID: 30852679
Cited by
-
The Role of Vitamin D in Combination Treatment for Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Jul 15;7:312. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00312. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32766259 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Management of Osteoporosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Review of the Literature and Practical Guide.Drugs Aging. 2019 Dec;36(12):1061-1072. doi: 10.1007/s40266-019-00714-4. Drugs Aging. 2019. PMID: 31541358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic efficacy of denosumab for rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2021 Dec 17;5(3):rkab099. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkab099. eCollection 2021. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2021. PMID: 34988358 Free PMC article.
-
Ukrainian Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults.Nutrients. 2024 Jan 16;16(2):270. doi: 10.3390/nu16020270. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38257163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kanis JA. Diagnosis of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis Int. 1997;7(S3):S108–S116. - PubMed
-
- Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, Wong JB, King A, Tosteson A. Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005–2025. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(3):465–475. - PubMed
-
- Lodder MC, Haugeberg G, Lems WF, et al. Oslo-Truro-Amsterdam (OSTRA) Collaborative Study Radiographic damage associated with low bone mineral density and vertebral deformities in rheumatoid arthritis: the Oslo-Truro-Amsterdam (OSTRA) collaborative study. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49(2):209–215. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

