Sublingual sufentanil (Zalviso) patient-controlled analgesia after total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective comparison with oxycodone with or without dexamethasone
- PMID: 30588072
- PMCID: PMC6299470
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S185197
Sublingual sufentanil (Zalviso) patient-controlled analgesia after total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective comparison with oxycodone with or without dexamethasone
Abstract
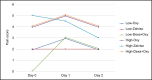
Postoperative pain is a major problem, especially in orthopedic surgery. Our data suggest suboptimal pain management after total knee arthroplasty. This study evaluated a sufentanil sublingual tablet system (Zalviso) to optimize postoperative pain treatment. This retrospective, single-center, cohort study was conducted between January 2017 and September 2017. Zalviso as standard treatment was compared with a cohort receiving oxycodone (Oxy) immediate release and Oxy extended release and another receiving Oxy immediate release, Oxy extended release, and dexamethasone (Dexa + Oxy). The primary end point, pain intensity, was assessed on a numeric rating scale (NRS). Highest, lowest, and number of NRS scores >7 were collected. Secondary end points included length of hospital stay, nausea, and mobilization on the day of surgery. Patients receiving Dexa + Oxy had a lower lowest-pain intensity on day 0 (median 0, IQR 0-0) when compared to patients receiving Oxy (median 2, IQR 0-3; P<0.0001) or Zalviso (median 2, IQR 0-4; P<0.0001). No differences were observed on day 1 or 2. No differences were observed in highest pain score or number of patients reporting NRS scores > 7. Patients treated with Dexa + Oxy or Zalviso were discharged earlier compared to patients treated with Oxy (P<0.001). Patients treated with Zalviso experienced more nausea compared to other groups on day 0 and day 1 (P<0.001). Patients treated with Dexa + Oxy had a higher percentage of mobilization on the day of surgery compared to Oxy and Zalviso (P<0.001). In conclusion, Zalviso did not improve postoperative pain management in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty and increased nausea.
Keywords: Zalviso; acute pain; multimodal treatment; opioid; postoperative pain; sublingual formulation; sublingual sufentanil tablet system; sufentanil; total knee arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780–785. - PubMed
-
- Patel A, Pavlou G, Mújica-Mota RE, Toms AD. The epidemiology of revision total knee and hip arthroplasty in England and Wales: a comparative analysis with projections for the United States. A study using the National Joint Registry dataset. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(8):1076–1081. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Y, Feng Y, Peng L. Effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2017;49(9):700–704. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources