Real-world evaluation of carboplatin plus a weekly dose of nab-paclitaxel for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 30588105
- PMCID: PMC6298387
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S189556
Real-world evaluation of carboplatin plus a weekly dose of nab-paclitaxel for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with interstitial lung disease
Abstract
Background: The optimal chemotherapy regimen for non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) remains unknown. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the real-world efficacy and safety of carboplatin (CBDCA) plus nab-paclitaxel (nab-PTX) as a first-line regimen for NSCLC patients with ILD.
Patients and methods: We retrospectively reviewed advanced NSCLC patients with ILD who had received CBDCA plus nab-PTX as a first-line chemotherapy regimen between April 2013 and March 2018. Patients were diagnosed with ILD based on the findings of a pretreatment high-resolution computed tomography of the chest.
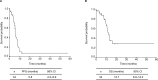
Results: The 34 patients enrolled in this study were included in the efficacy and safety analysis. Collagen vascular disease or a history of exposure to dust or asbestos was not reported for any patients. The median age of patients was 71 years (range, 59-83 years), and 32 patients had a performance status of 0 or 1. The overall response rate was 38.2%. The median progression-free survival and overall survival were 5.8 months and 12.7 months, respectively. Chemotherapy-related acute exacerbation of ILD was observed in two patients (5.7%). Other toxicities were feasible, and no treatment-related deaths occurred.
Conclusion: CBDCA plus nab-PTX, as a first-line chemotherapy regimen for NSCLC, showed favorable efficacy and safety in patients with preexisting ILD.
Keywords: carboplatin; interstitial lung disease; nab-paclitaxel; non-small-cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Efficacy and Safety of First-Line Chemotherapy in Patients With Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 8;10:1636. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01636. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33014824 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Evidence of Safety and Efficacy of Carboplatin plus Nanoparticle Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Preexisting Interstitial Lung Disease: A Retrospective Study.Can Respir J. 2019 Mar 20;2019:5315903. doi: 10.1155/2019/5315903. eCollection 2019. Can Respir J. 2019. PMID: 31015884 Free PMC article.
-
Phase II study of nab-paclitaxel + carboplatin for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and interstitial lung disease.Cancer Sci. 2019 Dec;110(12):3738-3745. doi: 10.1111/cas.14217. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31608537 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bevacizumab Plus Carboplatin Plus Nab-paclitaxel for Non-squamous Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in a Real-world Setting.Anticancer Res. 2023 Mar;43(3):1325-1330. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.16280. Anticancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36854522 Clinical Trial.
-
Anticancer drug treatment for advanced lung cancer with interstitial lung disease.Respir Investig. 2018 Jul;56(4):307-311. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Respir Investig. 2018. PMID: 29764748 Review.
Cited by
-
A phase II feasibility study of carboplatin and nab-paclitaxel for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with interstitial lung disease (YLOG0114).Thorac Cancer. 2022 May;13(9):1267-1275. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14376. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Thorac Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35322551 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nab-paclitaxel in combination with Bevacizumab in patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer after failure of at least one prior systemic regimen.J Cancer. 2020 Sep 13;11(21):6421-6428. doi: 10.7150/jca.47072. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33033525 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis induced by nab-paclitaxel: A rare complication.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 23;14:1094844. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1094844. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36909189 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy and Safety of First-Line Chemotherapy in Patients With Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 8;10:1636. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01636. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33014824 Free PMC article.
-
Pembrolizumab for Previously Untreated Patients with Advanced Non-small-cell Lung Cancer and Preexisting Interstitial Lung Disease.Intern Med. 2020 Aug 15;59(16):1939-1945. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4552-20. Epub 2020 May 8. Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32389949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Devesa SS, Bray F, Vizcaino AP, Parkin DM. International lung cancer trends by histologic type: male:female differences diminishing and adenocarcinoma rates rising. Int J Cancer. 2005;117(2):294–299. - PubMed
-
- Minegishi Y, Sudoh J, Kuribayasi H, et al. The safety and efficacy of weekly paclitaxel in combination with carboplatin for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Lung Cancer. 2011;71(1):70–74. - PubMed
-
- Shukuya T, Ishiwata T, Hara M, et al. Carboplatin plus weekly paclitaxel treatment in non-small cell lung cancer patients with interstitial lung disease. Anticancer Res. 2010;30(10):4357–4361. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous