Comparison of a micro-electro-mechanical system airflow sensor with the pneumotach in the forced oscillation technique
- PMID: 30588132
- PMCID: PMC6296186
- DOI: 10.2147/MDER.S181258
Comparison of a micro-electro-mechanical system airflow sensor with the pneumotach in the forced oscillation technique
Abstract
Purpose: This study supports the use of thin-film micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) airflow sensors in the forced oscillation technique.
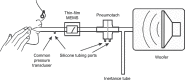
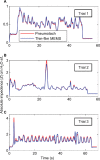
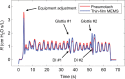
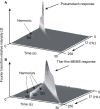
Materials and methods: The study employed static testing using air flow standards and computer-controlled sound attenuations at 8 Hz. Human feasibility studies were conducted with a testing apparatus consisting of a pneumotach and thin-film MEMS air flow sensors in series. Short-time Fourier transform spectra were obtained using SIGVIEW software.
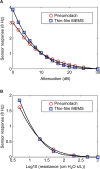
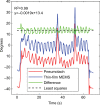
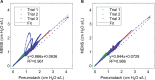
Results: Three tests were performed, and excellent correlations were observed between the probes. The thin-film MEMS probe showed superior sensitivity to higher frequencies up to 200 Hz.
Conclusion: The results suggest that lower-cost thin-film MEMS can be used for forced oscillation technique applications (including home care devices) that will benefit patients suffering from pulmonary diseases such as asthma, COPD, and cystic fibrosis.
Keywords: airway resistance; glottis closure; pulmonary disease; pulmonary impedance; short-time Fourier transform.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure CEF and REC are the owners of Feather Sensors, LLC, and XKX and SLM were employees of Feather Sensors, LLC at the time of this work. BPH was a graduate student of KRL (Boston University) during this work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Dubois AB, Brody AW, Lewis DH, Burgess BF. Oscillation mechanics of lungs and chest in man. J Appl Physiol. 1956;8(6):587–594. - PubMed
-
- Bates JH. Lung Mechanics: An Inverse Modeling Approach. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2009.
-
- Lutchen KR, Suki B. Understanding pulmonary mechanics using the forced oscillations technique. In: Khoo MCK, editor. Bioengineering Approaches to Pulmonary Physiology and Medicine. Boston, MA: Springer; 1996. pp. 227–253.
-
- Strömberg NO, Grönkvist MJ. Improved accuracy and extended flow range for a Fleisch pneumotachograph. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1999;37(4):456–460. - PubMed
-
- Kreit JW, Sciurba FC. The accuracy of pneumotachograph measurements during mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;154(4 Pt 1):913–917. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

