Elevated mRNA Levels of AURKA, CDC20 and TPX2 are associated with poor prognosis of smoking related lung adenocarcinoma using bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 30588191
- PMCID: PMC6299412
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.28728
Elevated mRNA Levels of AURKA, CDC20 and TPX2 are associated with poor prognosis of smoking related lung adenocarcinoma using bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
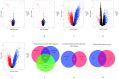
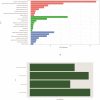
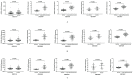
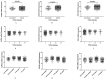
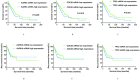
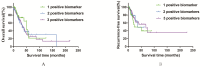
Background and aim: Adenocarcinoma is a very common pathological subtype for lung cancer. We aimed to identify the gene signature associated with the prognosis of smoking related lung adenocarcinoma using bioinformatics analysis. Methods: A total of five gene expression profiles (GSE31210, GSE32863, GSE40791, GSE43458 and GSE75037) have been identified from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were analyzed using GEO2R software and functional and pathway enrichment analysis. Furthermore, the overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) have been validated using an independent cohort from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Results: We identified a total of 58 DEGs which mainly enriched in ECM-receptor interaction, platelet activation and PPAR signaling pathway. Then according to the enrichment analysis results, we selected three genes (AURKA, CDC20 and TPX2) for their roles in regulating tumor cell cycle and cell division. The results showed that the hazard ratio (HR) of the mRNA expression of AURKA for OS was 1.588 with (1.127-2.237) 95% confidence interval (CI) (P=0.009). The mRNA levels of CDC20 (HR 1.530, 95% CI 1.086-2.115, P=0.016) and TPX2 (HR 1.777, 95%CI 1.262-2.503, P=0.001) were also significantly associated with the OS. Expression of these three genes were not associated with RFS, suggesting that there might be many factors affect RFS. Conclusion: The mRNA signature of AURKA, CDC20 and TPX2 were potential biomarkers for predicting poor prognosis of smoking related lung adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: Kaplan-Meier analysis; biomarkers; differentially expressed genes; gene ontology; lung adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Tanner NT, Kanodra NM, Gebregziabher M. et al. The association between smoking abstinence and mortality in the National Lung Screening Trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193:534–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

