Glucocorticoid-Inducible Kinase 2 Promotes Bladder Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Enhancing β-catenin/c-Myc Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 30588263
- PMCID: PMC6299383
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.25811
Glucocorticoid-Inducible Kinase 2 Promotes Bladder Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Enhancing β-catenin/c-Myc Signaling Pathway
Abstract
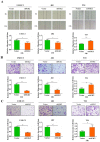
Background: Bladder cancer is one of the most common malignancies in urologic system. The glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 2 (SGK2) expression and function were largely unknown in cancers. Current study was aimed to investigate the role of SGK2 in bladder cancer and its potential mechanisms. Methods: SGK2 expression was quantified by western blot (WB) in multiple bladder cancer cell lines (T24, 5637, J82 and UMUC3) compared with normal urothelial cell line (SVHUC). SGK2 knocking down and overexpression model were established by lentivirus transfection. MTT, colony formation, wound healing and transwell assay were used to assess the tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion abilities, respectively. In addition, molecular function analysis was performed using FunRich software V3. Immunoprecipitation (IP) assay was applied to investigate the interaction between SGK2 and β-catenin at protein level. TCGA database was retrieved to verify the association between these genes and clinical tumor stage as well as prognosis among bladder cancer patients. Results: SGK2 expression was significantly upregulated in multiple bladder cancer cell lines compared with SVHUC at protein level. Cell proliferation, migration and invasion abilities were significantly decreased after knocking down SGK2 in J82 and UMUC3 cell lines. Inversely, cell aggressive phenotypes were significantly increased after overexpressing SGK2 in T24 cell line. Furthermore, functional analyses of SGK2 based on TCGA database showed that SGK2 related genes were involved in receptor activity, ATP binding, DNA repair protein, trans-membrane receptor activity and lipid binding. In addition, protein interaction analysis identified c-Myc was significantly enriched in SGK2 positively associated genes. The prediction was validated by WB and IP assay that SGK2 could directly bind with β-catenin at protein level to regulate their downstream gene c-Myc expression in bladder cancer to influence tumor progression. And clinical data generated from TCGA database also identified these downstream genes were significantly associated with tumor stage and survival status of bladder cancer patients. Conclusion: Taken together, our findings suggest SGK2 promotes bladder cancer progression via mediating β-catenin/c-Myc signaling pathway, which may serve as a potential therapeutic target for bladder cancer patients.
Keywords: bladder cancer; c-Myc; glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 2; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, Lerner SP, Malmstrom PU, Choi W. et al. Bladder cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:2796–810. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla V, Soundararajan R, Pao AC, Li H, Pearce D. Disinhibitory pathways for control of sodium transport: regulation of ENaC by SGK1 and GILZ. American journal of physiology-renal physiology. 2006;291:F714–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

