Serum microRNA-221 as a biomarker for diabetic retinopathy in patients associated with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 30588418
- PMCID: PMC6288522
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2018.12.02
Serum microRNA-221 as a biomarker for diabetic retinopathy in patients associated with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the candidate microRNA (miRNA), miR-221 as a novel biomarker for diabetic retinopathy (DR) in patients associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods: The subjects involved were divided into four groups: healthy control (HC), no diabetic retinopathy (NDR), non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) group. Serum miR-221 was validated by real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Also, serum angiotensin II (Ang II) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were examined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In addition, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was performed to explore the diagnostic accuracy of miR-221, Ang II and VEGF for DR in patients with T2D. Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was executed to estimate the correlations of serum miR-221 with metabolic parameters and serum markers in patients with T2D.
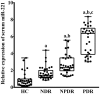
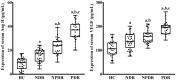
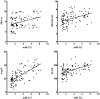
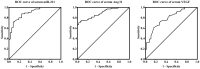
Results: Primarily, serum miR-221, Ang II and VEGF were increased significantly in T2D patients compared to HC participant respectively, and progressive up-regulated in NDR, NPDR and PDR groups (P<0.001). Additionally, miR-221 in serum was remarkably positively correlated with metabolic parameters such as glycated hemoglobin (r=0.310, P=0.002) and homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (r=0.413, P<0.001), as well as serum markers for instance Ang II (r=0.667, P<0.001) and VEGF (r=0.499, P<0.001). Furthermore, serum miR-221 (AUC, 0.894; 95%CI, 0.833-0.955; P<0.001), Ang II (AUC, 0.888; 95%CI, 0.828-0.949; P<0.001) and VEGF (AUC, 0.785; 95%CI, 0.695-0.875; P<0.001) had evidently diagnostic efficiency in DR, and miR-221 is the most effective among them.
Conclusion: Serum miR-221 as a potential biomarker could be related to not only occurrence but also progression for DR in patients with T2D. However, a prospective clinical trial is warranted.
Keywords: biomarker; diabetic retinopathy; microRNA-221; type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic and prognostic role of serum miR-20b, miR-17-3p, HOTAIR, and MALAT1 in diabetic retinopathy.IUBMB Life. 2019 Mar;71(3):310-320. doi: 10.1002/iub.1970. Epub 2018 Nov 23. IUBMB Life. 2019. PMID: 30468285
-
MicroRNA-126: a promising novel biomarker in peripheral blood for diabetic retinopathy.Int J Ophthalmol. 2017 Apr 18;10(4):530-534. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2017.04.05. eCollection 2017. Int J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28503423 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma level of miR-93 is associated with higher risk to develop type 2 diabetic retinopathy.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017 Jun;255(6):1159-1166. doi: 10.1007/s00417-017-3638-5. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28382439
-
Plasma miR-21 expression: an indicator for the severity of Type 2 diabetes with diabetic retinopathy.Biosci Rep. 2017 Mar 27;37(2):BSR20160589. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160589. Print 2017 Apr 28. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28108673 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of laser photocoagulation on serum angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, angiopoietin-1/angiopoietin-2 ratio, and soluble angiopoietin receptor Tie-2 levels in type 2 diabetic patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy.Int J Ophthalmol. 2014 Aug 18;7(4):648-53. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2014.04.11. eCollection 2014. Int J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25161936 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Long noncoding RNA GAS5 inhibits cell proliferation and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by sponging miR-221 and modulating SIRT1 expression.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Oct 20;11(20):8745-8759. doi: 10.18632/aging.102249. Epub 2019 Oct 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31631065 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-221/SIRT1/Nrf2 signal axis regulates high glucose induced apoptosis in human retinal microvascular endothelial cells.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Jul 22;20(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12886-020-01559-x. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32698791 Free PMC article.
-
Central role of podocytes in mediating cellular cross talk in glomerular health and disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Mar 1;326(3):F313-F325. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00328.2023. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38205544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating hsa-miR-221 as a possible diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of diabetic nephropathy.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Dec;50(12):9793-9803. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08846-y. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37831346 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA and diabetic retinopathy-biomarkers and novel therapeutics.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Aug;9(15):1280. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5189. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34532417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheung N, Mitchell P, Wong TY. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet. 2010;376(9735):124–136. - PubMed
-
- Antonetti DA, Klein R, Gardner TW. Diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(13):1227–1239. - PubMed
-
- Cheung N, Wong TY. Diabetic retinopathy and systemic vascular complications. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2008;27(2):161–176. - PubMed
-
- Cunha-Vaz J, Ribeiro L, Lobo C. Phenotypes and biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2014;41:90–111. - PubMed
-
- Simó R, Hernández C. Novel approaches for treating diabetic retinopathy based on recent pathogenic evidence. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015;48:160–180. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
