Recombination and identification of human alpha B-crystallin
- PMID: 30588422
- PMCID: PMC6288530
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2018.12.06
Recombination and identification of human alpha B-crystallin
Abstract
Aim: To recombine the human alpha B-crystallin (αB-crystallin) using gene cloning technology and prokaryotic expression vector and confirm the biological activity of recombinant human αB-crystallin.
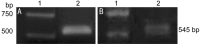
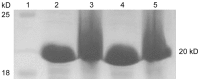
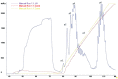
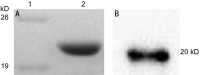
Methods: Cloning the human αB-crystallin cDNA according to the nucleotide sequence of the human αB-crystallin, constructing the pET-28/CRYAB prokaryotic expression plasmid by restriction enzyme digestion method, and stably expressing transformed into the Escherichia coli (E. coli) DH5 alpha. The recombinant human αB-crystallin was purified by Q sepharose. By enzyme digestion analysis, Western blotting and sequencing, the recombinant human αB-crystallin was identified and the activity of its molecular protein was detected.
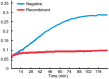
Results: Compared with the gene bank (GeneBank), the cloned human sequence of human αB-crystallin cDNA has the same open reading frame. Identification and sequencing of the cloned human αB-crystallin cDNA in prokaryotic expression vector confirmed the full length sequence, and the vector was constructed successfully. The E. coli containing plasmid pET-28/CRYAB induced by isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside successfully expressed the human αB-crystallin. Insulin confirmed that the recombinant human αB-crystallin has a molecular chaperone activity.
Conclusion: The prokaryotic expression vector pET-28/CRYAB of recombinant human αB-crystallin is successfully constructed, and the recombinant human αB-crystallin with molecular chaperone activity is obtained, which lay a foundation for the research and application of the recombinant human αB-crystallin and its chaperone activity.
Keywords: gene; human alpha B-crystallin; identification; recombination; vector construction.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differences in properties between human alphaA- and alphaB-crystallin proteins expressed in Escherichia coli cells in response to cold and extreme pH.Biochem J. 2003 Oct 15;375(Pt 2):471-5. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030748. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12826011 Free PMC article.
-
Site-directed mutations within the core "alpha-crystallin" domain of the small heat-shock protein, human alphaB-crystallin, decrease molecular chaperone functions.J Mol Biol. 1999 Jun 4;289(2):397-411. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2759. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10366513
-
Human αB-crystallin as fusion protein and molecular chaperone increases the expression and folding efficiency of recombinant insulin.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 19;13(10):e0206169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206169. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30339677 Free PMC article.
-
Functional sequences in human alphaB crystallin.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1860(1 Pt B):240-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.08.014. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26341790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamical structure of αB-crystallin.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014 Jul;115(1):11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.03.003. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24674783 Review.
References
-
- Srivastava OP, Srivastava K. Existence of deamidated alphaB-crystallin fragments in normal and cataractous human lenses. Mol Vis. 2003;9:110–118. - PubMed
-
- Mao YW, Liu JP, Xiang H, Li DW. Human alphaA- and alphaB-crystallins bind to Bax and Bcl-X(S) to sequester their translocation during staurosporine-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11(5):512–526. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi H, Miyagi M, Darrow RM, Crabb JS, Hollyfield JG, Organisciak DT, Crabb JW. Intense light exposure changes the crystallin content in retina. Exp Eye Res. 2003;76(1):131–133. - PubMed
-
- Kumar PA, Haseeb A, Suryanarayana P, Ehtesham NZ, Reddy GB. Elevated expression of alphaA- and alphaB-crystallins in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005;15; 444(2):77–83. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
