MicroRNA-8073: Tumor suppressor and potential therapeutic treatment
- PMID: 30589909
- PMCID: PMC6307750
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209750
MicroRNA-8073: Tumor suppressor and potential therapeutic treatment
Abstract
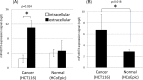
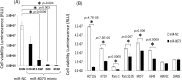
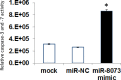
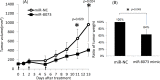
The comprehensive screening of intracellular and extracellular microRNAs was performed to identify novel tumor suppressors. We found that miR-8073 was present in exosome and predominantly exported from colorectal cancer cells. Treatment with a synthetic miR-8073 mimic resulted in a dramatic decrease in the proliferation of various types of cancer cells, which was not observed in similarly treated normal cells. As little is known about the biological functions of miR-8073, its target mRNAs were analyzed by both mRNA expression and in silico sequence analyses, leading to five probable target candidates (FOXM1, MBD3, CCND1, KLK10, and CASP2) that enhance survival during the regulation of the cell cycle, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. We experimentally confirmed that miR-8073 binds the 3'-UTR of each of these mRNA target candidates and that the introduction of a synthetic miR-8073 mimic into cancer cells reduced levels of protein expression. Finally, the antiproliferative effects of miR-8073 were validated in vivo: the subcutaneous injection of a synthetic miR-8073 mimic suppressed colorectal tumor volume to 43% in tumor-bearing xenografted mice. These results suggest that because miR-8073 binds, and thus reduces the levels of, these oncogenic targets, cancer cells must actively downregulate miR-8073 as a survival mechanism. The introduction of miR-8073 into tumors could thus inhibit tumor growth, indicating its great potential for cancer therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
At the time of the study, authors were full-time employees of Toray Industries, Inc. However, this does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



References
-
- Shimomura A, Shiino S, Kawauchi J, Takizawa S, Sakamoto H, Matsuzaki J, Ono M, Takeshita F, Niida S, Shimizu C, Fujiwara Y, Kinoshita T, Tamura K, Ochiya T., et al. (2016) Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting breast cancer in the early stage. Cancer Sci. 107(3):326–34 10.1111/cas.12880 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

