REV-ERBα Regulates TH17 Cell Development and Autoimmunity
- PMID: 30590045
- PMCID: PMC6400287
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.11.101
REV-ERBα Regulates TH17 Cell Development and Autoimmunity
Abstract
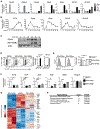
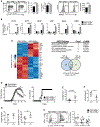
RORγt is well recognized as the lineage-defining transcription factor for T helper 17 (TH17) cell development. However, the cell-intrinsic mechanisms that negatively regulate TH17 cell development and autoimmunity remain poorly understood. Here, we demonstrate that the transcriptional repressor REV-ERBα is exclusively expressed in TH17 cells, competes with RORγt for their shared DNA consensus sequence, and negatively regulates TH17 cell development via repression of genes traditionally characterized as RORγt dependent, including Il17a. Deletion of REV-ERBα enhanced TH17-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, exacerbating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) and colitis. Treatment with REV-ERB-specific synthetic ligands, which have similar phenotypic properties as RORγ modulators, suppressed TH17 cell development, was effective in colitis intervention studies, and significantly decreased the onset, severity, and relapse rate in several models of EAE without affecting thymic cellularity. Our results establish that REV-ERBα negatively regulates pro-inflammatory TH17 responses in vivo and identifies the REV-ERBs as potential targets for the treatment of TH17-mediated autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: IL-17A; REV-ERB; RORγt; SR9009; T cells; Th17; autoimmunity; circadian.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





References
-
- Bronner SM, Zbieg JR, and Crawford JJ (2017). RORg antagonists and inverse agonists: a patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat 27, 101–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

